南康网站建设公司b2b和b2c是什么意思
前提知识:[Pytorch] 前向传播和反向传播示例_友人小A的博客-CSDN博客
目录
简介
叶子节点
Tensor AutoGrad Functions
简介
torch.autograd是PyTorch的自动微分引擎(自动求导),为神经网络训练提供动力。torch.autograd需要对现有代码进行最少的更改——声明需要计算梯度的Tensor的属性requires_grad=True。截至目前,PyTorch仅支持 FloatTensor类型(half、float、double和bfloat16)和 ComplexTensor(cfloat、cdouble)的autograd。【信息来自官网】
叶子节点
叶子结点是离散数学中的概念。一棵树当中没有子结点(即度为0)的结点称为叶子结点,简称“叶子”。 叶子是指出度为0的结点,又称为终端结点。
在pytorch中,什么是叶子节点?根据官方定义理解如下。
- 所有requires_grad为False的张量,都约定俗成地归结为叶子张量
- requires_grad为True的张量, 如果他们是由用户创建的,则它们是叶张量(leaf Tensor), 表明不是运算的结果,因此grad_fn=None
示例1
def test_training_pipeline2():input_data = [[4, 4, 4, 4],[9, 9, 9, 9]] # 2x4input = torch.tensor(input_data, dtype=torch.float32) # requires_grad=Falseoutput = torch.sqrt(input)target_data = [1, 2, 3, 4]target = torch.tensor(target_data, dtype=torch.float32) # requires_grad=Falseloss_fn = torch.nn.MSELoss()loss = loss_fn(input=output, target=target)print("\ninput.is_leaf:", input.is_leaf)print("output.requires_grad:", output.requires_grad)print("output.is_leaf:", output.is_leaf)print("target.is_leaf:", target.is_leaf)print("loss.requires_grad:", loss.requires_grad)print("loss.is_leaf:", loss.is_leaf)
样例2
def test_training_pipeline2():input_data = [[4, 4, 4, 4],[9, 9, 9, 9]] # 2x4input = torch.tensor(input_data, dtype=torch.float32) # requires_grad=Falseoutput = torch.sqrt(input)output.requires_grad_(True) # requires_grad=Truetarget_data = [1, 2, 3, 4]target = torch.tensor(target_data, dtype=torch.float32) # requires_grad=Falseloss_fn = torch.nn.MSELoss()loss = loss_fn(input=output, target=target)print("\ninput.is_leaf:", input.is_leaf)print("output.requires_grad:", output.requires_grad)print("output.is_leaf:", output.is_leaf)print("target.is_leaf:", target.is_leaf)print("loss.requires_grad:", loss.requires_grad)print("loss.is_leaf:", loss.is_leaf)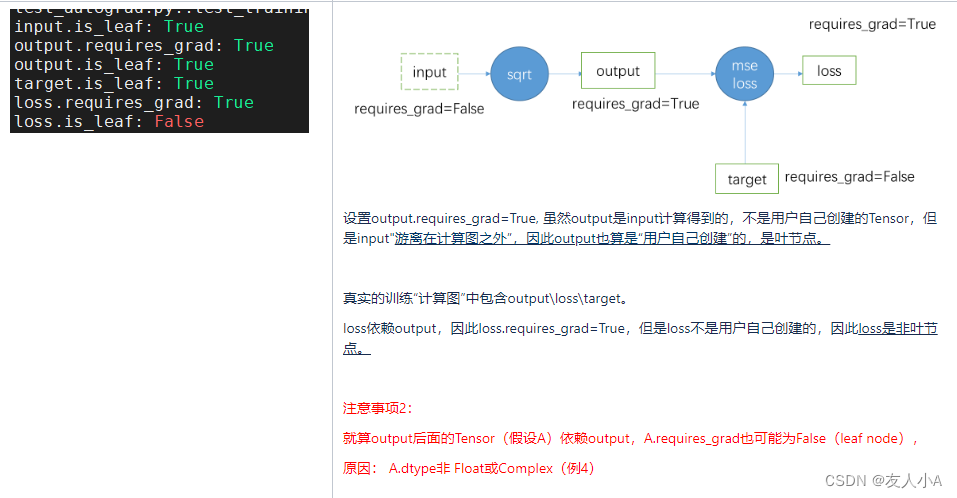
样例3
def test_training_pipeline5():input = torch.rand(1, requires_grad=True)output = torch.unique(input=input, sorted=True, return_inverse=False, return_counts=False, dim=None)print("\ninput.is_leaf:", input.is_leaf)print("output.requires_grad:", output.requires_grad)print("output.is_leaf:", output.is_leaf)output.backward()样例4
def test_training_pipeline3():input_data = [[4, 4, 4, 4],[9, 9, 9, 9]] # 2x4input_a = torch.tensor(input_data, dtype=torch.float32, requires_grad=True)input_b = torch.tensor(input_data, dtype=torch.float32, requires_grad=True)output = torch.ne(input_a, input_b)print("\ninput_a.is_leaf:", input_a.is_leaf)print("input_b.is_leaf:", input_b.is_leaf)print("output.dtype:", output.dtype)print("output.requires_grad:", output.requires_grad)print("output.is_leaf:", output.is_leaf)output.backward() # 报错
样例5
def test_training_pipeline7():input_data = [[4, 4, 4, 4],[9, 9, 9, 9]] # 2x4input_a = torch.tensor(input_data, dtype=torch.float32, requires_grad=True)input_b = torch.tensor(input_data, dtype=torch.float32) output = torch.add(input_a, input_b)print("\ninput_a.requires_grad:", input_a.requires_grad)print("input_b.requires_grad:", input_b.requires_grad)print("output.requires_grad:", output.requires_grad)print("output.is_leaf:", output.is_leaf)grad = torch.ones_like(output)input_b[0][0] = 10 input_a[0][0] = 10 output.backward(grad)样例6
def test_training_pipeline9():x = torch.tensor([1.0], requires_grad=True)y = x + 2z = 2 * y # <-- dz/dy=2y[0] = -2.0print("\nx.is_leaf:", x.is_leaf)print("y.is_leaf:", y.is_leaf)print("z.is_leaf:", z.is_leaf)print("\nx.requires_grad:", x.requires_grad)print("y.requires_grad:", y.requires_grad)print("z.requires_grad:", z.requires_grad)z.backward()def test_training_pipeline9():x = torch.tensor([1.0], requires_grad=True)y = x + 2z = y * y # <-- dz/dy= 2*yy[0] = -2.0print("\nx.is_leaf:", x.is_leaf)print("y.is_leaf:", y.is_leaf)print("z.is_leaf:", z.is_leaf)print("\nx.requires_grad:", x.requires_grad)print("y.requires_grad:", y.requires_grad)print("z.requires_grad:", z.requires_grad)z.backward()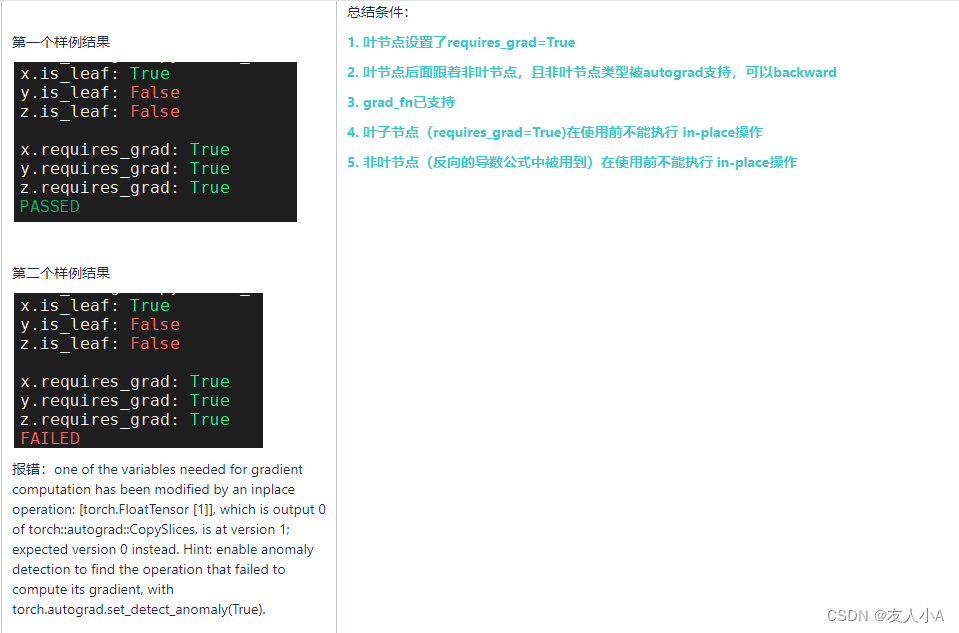
Tensor AutoGrad Functions
-
Tensor.grad
-
Tensor.requires_grad
-
Tensor.is_leaf
-
Tensor.backward(gradient=None, reqain_graph=None, create_graph=False)
-
Tensor.detach()
-
Tensor.detach_()
-
Tensor.retain_grad()



