怎么为自己做的网站申请域名推广链接点击器app
目录
1、本次需要实现的3个类即接口总览
2、list的模拟实现
2.1 链表结点的设置以及初始化
2.2 链表的迭代器
2.3 容量接口及默认成员函数
1、本次需要实现的3个类即接口总览
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
struct __List_node//创建一个T类型的链表结点
{__List_node(const T& data = T());//构造函数__List_node<T>* _next;__List_node<T>* _prev;T _data;
};
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __List_iterator//封装链表的迭代器
{typedef __List_node<T> Node;typedef __List_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;//成员变量__List_iterator(Node* node);//构造函数。将迭代器中的结点初始化成传过来的结点//各种运算符重载函数Ref operator*();Ptr operator->();Self& operator++();Self operator++(int);Self& operator--();Self operator--(int);bool operator!=(const Self& it);
};
template<class T>
class List//真正的链表
{
public:typedef __List_node<T> Node;//将链表结点的名称重命名为Nodetypedef __List_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __List_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;//带头双向循环链表//默认成员函数List();~List();List(const List<T>& lt);List<T>& operator=(List<T> lt);//插入删除函数void clear();//clear是清除除了头节点意外的所以结点void push_back(const T& x);//一定要用引用,因为T不一定是内置类型void pop_back();void push_front(const T& x);void pop_front();void insert(iterator pos, const T& x);void erase(iterator pos);//迭代器相关函数iterator begin();iterator end();const_iterator begin() const;const_iterator end() const;
private:Node* _head;
};2、list的模拟实现
2.1 链表结点的设置以及初始化
list是双向带头循环链表,所以链表的结点的成员变量需要有一个数值,一个指向前一个结点的指针,一个指向后一个结点的指针。初始化时,需要创建一个不存放有效值的头节点,并让头节点的两个指针都指向自己
链表的成员变量只需要一个指向头节点的指针
结点的结构体当中也需要创建一个构造函数,因为在创建结点时可以传入值
template<class T>
struct __List_node//创建一个T类型的链表结点
{__List_node(const T& data = T())//构造函数:_data(data), _next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr){}__List_node<T>* _next;__List_node<T>* _prev;T _data;
};List()
{_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;
}上面的构造函数一定要使用引用,因为T不一定是内置类型
2.2 链表的迭代器
在上面的总览中可以看到链表的迭代器倍封装成了一个类,并且这个类有3个参数
首先,解释为什么会倍封装成一个类呢?
在vector中,迭代器就是一个指针,当我们对这个指针解引用(即*),就可以拿到这个指针所指向的数据,对其++,就可以让指针往下一个数据走,但在list中不行。如果迭代器是指向一个结点的指针,那么当对这个指针解引用时,拿到的是一个类对象,即这个结点本身,并不能拿到其中的数据,当对这个指针++时,并不能往下一个结点走所以我们需要将迭代器封装成一个类,这个类中的成员变量仍然是一个指向结点的指针,只是我们会重载一下里面的运算符,让我们*或++等操作的时候,能够直接拿到里面的数据和让指针往下一个结点。所以我们封装这个类的原因,就是为了让我们在使用list时,与使用vector等是一样的,即更加方便。实际上,迭代器这个类里面的成员变量仍然是一个指向结点的指针。
其次,解释为什么会有3个参数呢?
我们可以看到在链表类中会对迭代器进行重命名
typedef __List_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef __List_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;因为我们对于list和const list调用的迭代器是不同的,若我们只有一个参数T,那这个时候我们重命名是没办法重命名两个的,也就是说,若只有一个参数,则需要封装两个迭代器的类,而这两个类中只有operator*和operator->是不同的,所以弄成3个参数会更好一些。
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __List_iterator//封装链表的迭代器
{typedef __List_node<T> Node;typedef __List_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;//成员变量__List_iterator(Node* node)//构造函数。将迭代器中的结点初始化成传过来的结点:_node(node){}// *itRef operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}// ++itSelf& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}// it++Self operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);//调用默认的拷贝构造,因为是指针类型所以直接用默认的//_node = _node->_next;++(*this);return tmp;}// --itSelf& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}// it--Self operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);//_node = _node->_prev;--(*this);return tmp;}// it != end()bool operator!=(const Self& it){return _node != it._node;}
};iterator begin()
{return iterator(_head->_next);//使用这个结点去构造一个迭代器,并将这个迭代器返回
}
iterator end()
{return iterator(_head);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{return const_iterator(_head->_next);//使用这个结点去构造一个迭代器,并将这个迭代器返回
}
const_iterator end() const
{return const_iterator(_head);
}当我们是list调用begin是,则会调用返回值是iterator的,而iterator是__List_iterator<T, T&, T*>的,也就是调用*和->时,拿到的都是可读可写的值,反之则是只读的
int main()
{//对于内置类型List<int> lt;lt.push_back(1);lt.push_back(2);lt.push_back(3);lt.push_back(4);List<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){cout << *it << " ";it++;}return 0;
}class Date
{
public:int _year = 0;int _month = 1;int _day = 1;
};
int main()
{//对于自定义类型List<Date> lt;lt.push_back(Date());lt.push_back(Date());List<Date>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){cout << it->_year << " " << it->_month << " " << it->_day << endl;//也可以cout << (*it)._year << " " << (*it)._month << " " << (*it)._day << endl;it++;}return 0;
}->通常是在链表中存储的是自定义类型才会使用,通过上面可知->返回的是这个结构体的数值域的地址,那不应该是it->->_year吗(因为前面的it->返回后是Date*)?为了可读性,倍编译器处理了一下
这里说明一下begin和end返回的结点分别是那个
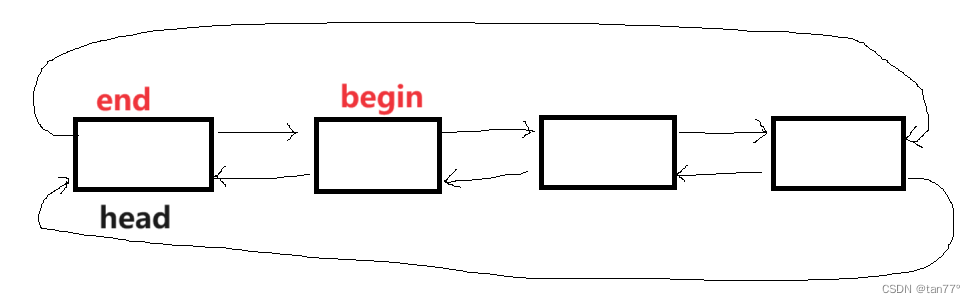
2.3 容量接口及默认成员函数
~List()
{clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;
}
List(const List<T>& lt)
{_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;//const_iterator it = lt.begin();//这里迭代器不需要指定是那个类域,因为就是在这个类中使用//while (it != lt.end())//{// push_back(*it);// ++it;//}for (auto e : lt)//这里与上面用迭代器一样,因为最终也会被替换成迭代器push_back(e);
}
/*List<T>& operator=(const List<T>& lt)
{if (this != <){clear();for (ayto e : lt)push_back(e);}return *this;
}*/
List<T>& operator=(List<T> lt)
{swap(_head, lt._head);//原来的空间给这个临时变量,因为这个临时变量是自定义类型,出了作用域后会自动调用析构函数return *this;
}
void clear()//clear是清除除了头节点意外的所以结点
{iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){erase(it++);}
}
void push_back(const T& x)//一定要用引用,因为T不一定是内置类型
{Node* tail = _head->_prev;Node* newnode = new Node(x);tail->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = tail;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_prev = newnode;/*insert(end(),x);*/
}
void pop_back()
{Node* tail = _head->_prev;Node* prev = tail->_prev;delete tail;_head->_prev = prev;prev->_next = _head;//erase(--end());
}
void push_front(const T& x)
{Node* first = _head->_next;Node* newnode = new Node(x);_head->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = _head;newnode->_next = first;first->_prev = newnode;//insert(begin(), x);
}
void pop_front()
{Node* first = _head->_next;Node* second = first->_next;delete first;_head->_next = second;second->_prev = _head;//erase(begin());
}
void insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{Node* newnode = new Node(x);Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;prev->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;
}
void erase(iterator pos)
{assert(pos != end());//不能删除头节点Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* next = cur->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;cur = nullptr;
}template<class T>
struct __List_node//创建一个T类型的链表结点
{__List_node(const T& data = T())//构造函数:_data(data), _next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr){}__List_node<T>* _next;__List_node<T>* _prev;T _data;
};
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __List_iterator//封装链表的迭代器
{typedef __List_node<T> Node;typedef __List_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;//成员变量__List_iterator(Node* node)//构造函数。将迭代器中的结点初始化成传过来的结点:_node(node){}// *itRef operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}// ++itSelf& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}// it++Self operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);//调用默认的拷贝构造,因为是指针类型所以直接用默认的//_node = _node->_next;++(*this);return tmp;}// --itSelf& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}// it--Self operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);//_node = _node->_prev;--(*this);return tmp;}// it != end()bool operator!=(const Self& it){return _node != it._node;}
};
template<class T>
class List//真正的链表
{
public:typedef __List_node<T> Node;//将链表结点的名称重命名为Nodetypedef __List_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __List_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;//带头双向循环链表List(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}~List(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}List(const List<T>& lt){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;//const_iterator it = lt.begin();//这里迭代器不需要指定是那个类域,因为就是在这个类中使用//while (it != lt.end())//{// push_back(*it);// ++it;//}for (auto e : lt)//这里与上面用迭代器一样,因为最终也会被替换成迭代器push_back(e);}/*List<T>& operator=(const List<T>& lt){if (this != <){clear();for (ayto e : lt)push_back(e);}return *this;}*/List<T>& operator=(List<T> lt){swap(_head, lt._head);//原来的空间给这个临时变量,因为这个临时变量是自定义类型,出了作用域后会自动调用析构函数return *this;}void clear()//clear是清除除了头节点意外的所以结点{iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){erase(it++);}}void push_back(const T& x)//一定要用引用,因为T不一定是内置类型{Node* tail = _head->_prev;Node* newnode = new Node(x);tail->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = tail;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_prev = newnode;/*insert(end(),x);*/}void pop_back(){Node* tail = _head->_prev;Node* prev = tail->_prev;delete tail;_head->_prev = prev;prev->_next = _head;//erase(--end());}void push_front(const T& x){Node* first = _head->_next;Node* newnode = new Node(x);_head->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = _head;newnode->_next = first;first->_prev = newnode;//insert(begin(), x);}void pop_front(){Node* first = _head->_next;Node* second = first->_next;delete first;_head->_next = second;second->_prev = _head;//erase(begin());}void insert(iterator pos, const T& x){Node* newnode = new Node(x);Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;prev->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;}void erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end());//不能删除头节点Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* next = cur->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;cur = nullptr;}iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);//使用这个结点去构造一个迭代器,并将这个迭代器返回}iterator end(){return iterator(_head);}const_iterator begin() const{return const_iterator(_head->_next);//使用这个结点去构造一个迭代器,并将这个迭代器返回}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(_head);}
private:Node* _head;
};