手机wap网站制作seo培训一对一
文章目录
- 一、工厂模式(三种)
- 1.简单工厂模式
- 1.1 概念:
- 1.2 `使用场景`:
- 1.3 模型图解:
- 1.4 伪代码:
- 2.工厂方法模式
- 2.1 概念:
- 2.2 `使用场景`:
- 2.3 模型图解:
- 2.4 伪代码
- 3.抽象工厂模式
- 3.1 概念
- 3.2 `使用场景`
- 3.3 模型图解:以两层模型做例子
- 3.4 伪代码
- 3.4.1 以品牌角度设计工厂
- 3.4.2 以手机角度设计工厂
- 3.5 实战:抽象工厂 + 简单工厂模式 +策略模式
- 3.5.1 业务方法调用
- 3.5.2 抽象工厂创建二级工厂,定义获取业务对象接口(二级工厂去创建具体的业务对象)
- 3.5.3 二级工厂 获得对象
- 3.5.3 二级工厂 具体的业务对象
- 3.5.3 处理的业务
- 补充:6大设计原则
- 3.6 总结:
一、工厂模式(三种)
1.简单工厂模式
1.1 概念:
通过一个工厂类来创建对象,根据不同的参数或条件返回相应的对象实例。
隐藏了对象的创建细节,客户端只需通过工厂类获取对象而不需要直接实例化对象。
1.2 使用场景:
使用者:根据不同的参数或条件返回相应的对象实例
1.3 模型图解:
角色:手机总工厂、参数、手机、小米手机、华为手机
后续补充:
1.4 伪代码:
public class SimpleFactoryTest {static class SimpleFactory {static SimpleFactoryTest.Mobile createMobile(int mobileType) throws Exception {if (mobileType == 1) {return new SimpleFactoryTest.HuaWei();} else if (mobileType == 2) {return new SimpleFactoryTest.XiaoMi();} else {throw new Exception("手机类型不存在!!!");}}}public static class Mobile {protected void call() {System.out.println("mobile...");}}public static class HuaWei extends Mobile {public void call() {System.out.println("huaWei...");}}public static class XiaoMi extends Mobile {public void call() {System.out.println("xiaomi...");}}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {SimpleFactoryTest.Mobile mobile = SimpleFactory.createMobile(1);mobile.call();}
}
2.工厂方法模式
2.1 概念:
定义了一个创建对象的接口,具体对象的创建由对象工厂决定。
使得对象的创建延迟到子类工厂,从而实现了对扩展开放、对修改关闭的原则。
2.2 使用场景:
使用者:根据不同的子工厂创建相应的对象实例
2.3 模型图解:
角色:手机总工厂、小米手机工厂、华为手机工厂、手机、小米手机、华为手机
后续补充
2.4 伪代码
public class FactoryMethodTest {interface FactoryMethod {Mobile createMobile();}static class HuaweiFactory implements FactoryMethod {@Overridepublic Mobile createMobile() {return new Huawei();}}static class XiaomiFactory implements FactoryMethod {@Overridepublic Mobile createMobile() {return new Xiaomi();}}static class Mobile {protected void call() {System.out.println("mobile...");}}static class Huawei extends Mobile {@Overridepublic void call() {System.out.println("huawei...");}}static class Xiaomi extends Mobile {@Overridepublic void call() {System.out.println("xiaomi...");}}public static void main(String[] args) {final HuaweiFactory huaweiFactory = new HuaweiFactory();final Mobile mobile = huaweiFactory.createMobile();mobile.call();}
}
3.抽象工厂模式
3.1 概念
抽象工厂模式提供一个接口,用于创建一系列相关或相互依赖的对象。
通过使用抽象工厂及其产品接口来创建对象,从而将客户端与具体的产品实现解耦。
3.2 使用场景
适用:三层关系
| 产品 | 品牌 | 子品牌 |
|---|---|---|
| 手机 | 华为手机 | Mate60 / P60手机 …等 |
| 手机 | 小米手机 | 红米 / Note2 手机 … 等 |
适用:两层关系
| 产品 | 品牌 |
|---|---|
| 手机 | 华为 |
| 电脑 | 小米 |
3.3 模型图解:以两层模型做例子
角色::总工厂、小米工厂、华为工厂、小米手机、华为手机、小米路由器、华为路由器
3.4 伪代码
3.4.1 以品牌角度设计工厂
/*** descr: 以品牌角度设计工厂** @date: 2024/1/24**/
public interface AbstractFactory {Phone createPhone();Computer createComputer();class HuaweiFactory implements AbstractFactory {@Overridepublic Phone createPhone() {return new HuaweiPhone();}@Overridepublic Computer createComputer() {return new HuaweiComputer();}}class XiaomiFactory implements AbstractFactory {@Overridepublic Phone createPhone() {return new XiaomiPhone();}@Overridepublic Computer createComputer() {return new XiaomiComputer();}}class HuaweiPhone implements Phone {@Overridepublic void call() {System.out.println("huawei call...");}}class HuaweiComputer implements Computer {@Overridepublic void play() {System.out.println("huawei play...");}}class XiaomiPhone implements Phone {@Overridepublic void call() {System.out.println("xiaomi play...");}}class XiaomiComputer implements Computer {@Overridepublic void play() {System.out.println("xiaomi play...");}}interface Phone {void call();}interface Computer {void play();}
}3.4.2 以手机角度设计工厂
代码目录结构:
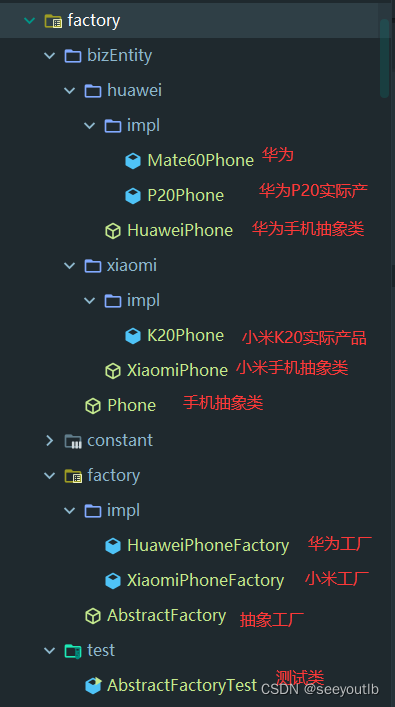
1.测试类 及常量类
1.1 测试类
/*** descr** @author: bjh* @date: 2024/1/27**/
public class AbstractFactoryTest {public static void main(String[] args) {doBiz(Constant.BRAND_HUAWEI, Constant.MODEL_HUAWEI_MATE60);doBiz(Constant.BRAND_XIAOMI, Constant.MODEL_XIAOMI_K20);}/*** 业务方法:** @param brand 品牌* @param modelName 机型*/public static void doBiz(String brand, String modelName) {final AbstractFactory factory = AbstractFactory.getFactory(brand);final Phone phone = factory.createPhone(modelName);phone.call();}}
1.2 常量类
/*** descr:便于管理和维护魔法值** @author: bjh* @date: 2024/1/27**/
public interface Constant {String BRAND_HUAWEI = "huawei";String BRAND_XIAOMI = "xiaomi";String MODEL_HUAWEI_MATE60 = "mate60";String MODEL_HUAWEI_P20 = "p20";String MODEL_XIAOMI_K20 = "k20";
}2.抽象工厂
/*** descr: 抽象总工厂;* 1.采用简单工厂方法模式获得二级工厂* 2.定义创建手机的接口方法** @author: bjh* @date: 2024/1/26**/
public abstract class AbstractFactory {public abstract Phone createPhone(String modalName);public static AbstractFactory getFactory(String brand) {// 此处三木运算符使用不严谨,实际编码不建议这样写return Constant.BRAND_HUAWEI.equals(brand) ? new HuaweiPhoneFactory() : new XiaomiPhoneFactory();}
}3.二级工厂(实际工厂)
3.1 华为手机工厂
/*** descr: 华为手机工厂,生成华为手机** @author: bjh* @date: 2024/1/27**/
public class HuaweiPhoneFactory extends AbstractFactory {@Overridepublic Phone createPhone(String modalName) {// 此处三木运算符使用不严谨,实际编码不建议这样写return Constant.MODEL_HUAWEI_MATE60.equals(modalName) ? new Mate60Phone() : new P20Phone();}
}
3.2 小米手机工厂
/*** descr** @author: bjh* @date: 2024/1/27**/
public class XiaomiPhoneFactory extends AbstractFactory {@Overridepublic Phone createPhone(String modalName) {// 此处写法不严谨,实际编码不建议这样写return new K20Phone();}
}
4.抽象手机
/*** descr:手机产品** @author: bjh* @date: 2024/1/26**/
public abstract class Phone {// 机型名称protected String modelName;// 是否支持卫星通话:小米不支持,华为支持protected Boolean satellitePhone;// 公有业务方法:策略模式abstract public void call();
}
5.华为抽象手机与小米抽象手机
5.1 华为抽象手机
/*** descr:抽象的华为手机,定义华为手机特有的业务** @author: bjh* @date: 2024/1/26**/
public abstract class HuaweiPhone extends Phone {// 定义华为手机相关业务: 拨打卫星电话protected abstract void callSatellite();// 支持卫星电话private Boolean satellitePhone = true;
}5.2 小米抽象手机
/*** descr:抽象的小米手机,定义小米手机特有的业务** @author: bjh* @date: 2024/1/26**/
public abstract class XiaomiPhone extends Phone {//小米手机便宜protected String cheap = "有点便宜!";//不支持卫星电话private Boolean satellitePhone = false;
}
- 实际手机产品:mate60、p20、k20
6.1 mate60
/*** descr 实际华为产品:mate60** @author: bjh* @date: 2024/1/27**/
public class Mate60Phone extends HuaweiPhone {private String modelName = "华为mate60";@Overridepublic void call() {System.out.println(this.modelName + "拨打电话...");}@Overrideprotected void callSatellite() {System.out.println(this.modelName + " >> 拨打卫星电话");}
}6.2 p20
/*** descr 实际华为产品:P20** @author: bjh* @date: 2024/1/27**/
public class P20Phone extends HuaweiPhone {private String modelName = "华为P20";@Overridepublic void call() {System.out.println(this.modelName + "拨打电话...");}@Overrideprotected void callSatellite() {System.out.println(this.modelName + ">> 拨打卫星电话");}
}6.3 k20
/*** descr 实际小米产品:K20** @author: bjh* @date: 2024/1/27**/
public class K20Phone extends XiaomiPhone {private String modelName = "小米K20";@Overridepublic void call() {// 抽取变量提高代码可维护性,HashMap源码中有类似这样写法String modalName = this.modelName;System.out.println(modalName + super.cheap);System.out.println(modalName + "拨打电话...");}
}3.5 实战:抽象工厂 + 简单工厂模式 +策略模式
代码目录结构:
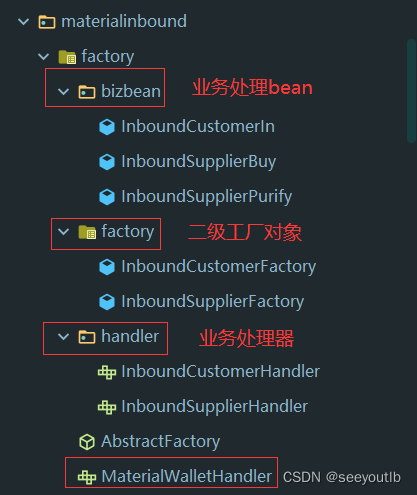
3.5.1 业务方法调用
/*** 根据业务类型计算真正需要动账的存欠类型** @param materialInboundDO* @param walletTypeAndWeight* @return*/private Map<String, BigDecimal> doBizType(MaterialInboundDO materialInboundDO, Map<String, BigDecimal> walletTypeAndWeight) {final AbstractFactory factory = AbstractFactory.getFactory(materialInboundDO.getBillType());final MaterialWalletHandler materialInboundBean = factory.getMaterialInboundOutboundBean(materialInboundDO.getBizType());return materialInboundBean.doBizType(walletTypeAndWeight);}
3.5.2 抽象工厂创建二级工厂,定义获取业务对象接口(二级工厂去创建具体的业务对象)
/*** 抽象工厂解决供应商/客户来料不同的业务类型对客户钱包的动账变化** @date: 2023/7/18**/
public abstract class AbstractFactory {/*** 获得单据类型工厂** @param billType 单据类型* @return*/public static AbstractFactory getFactory(String billType) {if (BillTypeEnum.MATERIAL_CUSTOMER_IN.getKey().equals(billType)) {return new InboundCustomerFactory();} else if ( BillTypeEnum.MATERIAL_SUPPLIER_IN.getKey().equals(billType)) {return new InboundSupplierFactory();} else if (BillTypeEnum.MATERIAL_CUSTOMER_OUT.getKey().equals(billType)) {return new OutboundCustomerFactory();} else if (BillTypeEnum.MATERIAL_SUPPLIER_OUT.getKey().equals(billType)) {return new OutboundSupplierFactory();}throw new ServiceException("原料业务工厂不存在");}/*** 获得业务对象** @param bizType 业务类型* @return*/public abstract MaterialWalletHandler getMaterialInboundOutboundBean(String bizType);
}3.5.3 二级工厂 获得对象
/*** descr 客户来料工厂** @date: 2023/7/18**/
public class InboundCustomerFactory extends AbstractFactory {@Overridepublic InboundCustomerHandler getMaterialInboundOutboundBean(String bizType) {if (BizTypeEnum.M_CUSTOMER_IN.getKey().equals(bizType)) {return new InboundCustomerIn();}throw new ServiceException("客户来料业务类型不存在");}
}
3.5.3 二级工厂 具体的业务对象
/*** descr 客户:客户来料** @date: 2023/7/18**/
public class InboundCustomerIn implements InboundCustomerHandler {@Overridepublic Map<String, BigDecimal> doBizType(Map<String, BigDecimal> walletTypeAndWeight) {return walletTypeAndWeight;}
}
3.5.3 处理的业务
顶层接口,如下子业务处理方式
/*** descr 来料/出料业务定义接口** @date: 2023/7/18**/
public interface MaterialWalletHandler {Map<String, BigDecimal> doBizType(Map<String, BigDecimal> walletTypeAndWeight);}

中间层子接口之一:用于规范业务
/*** descr 客户来料接口** @date: 2023/7/18**/
public interface InboundCustomerHandler extends MaterialWalletHandler {}
中间层接口实现1:用于处理业务
/*** descr 客户:客户来料** @date: 2023/7/18**/
public class InboundCustomerIn implements InboundCustomerHandler {@Overridepublic Map<String, BigDecimal> doBizType(Map<String, BigDecimal> walletTypeAndWeight) {return walletTypeAndWeight;}
}
中间层接口实现2:用于处理业务
/*** descr 供应商:发料兑料** @date: 2023/7/18**/
public class OutboundSupplierMix implements OutboundSupplierHandler {@Overridepublic Map<String, BigDecimal> doBizType(Map<String, BigDecimal> walletTypeAndWeight) {final HashMap<String, BigDecimal> walletTypeAndWeightMap = new HashMap<>(walletTypeAndWeight);walletTypeAndWeightMap.remove(WalletTypeEnum.CASH.getKey());return walletTypeAndWeightMap;}
}
补充:6大设计原则
1.单一职责
2.开放封闭
3.接口隔离
4.里氏替换
5.依赖倒置
6.迪米特法则
转送:java常用设计模式
3.6 总结:
- 以上实战中,代码没有写的很完美,还有许多改善的地方
- 抽象工厂在实际运用中比一般都例子都相对复杂;或可能写的理解的有所欠缺
- 抽象工厂定义了对象怎么创建;策略模式定义了业务怎么实现
- 一般抽象工厂模式都想要依托简单工厂或工厂方法模式创建二级工厂;在实践中一般会搭配策略模式或模板方法模式去处理相关业务
- 设计模式的使用主要是对业务代码进行简化或抽象,尽量符合6大设计原则;在技术人员沟通中,只要说出某种设计模式,就能知道业务大概是怎么处理的,极大的减少了沟通成本
