信用网站建设工作总结seochan是什么意思
 限时开放,猛戳订阅! 👉 《一起玩蛇》🐍
限时开放,猛戳订阅! 👉 《一起玩蛇》🐍
💭 写在前面: 本篇是关于多伦多大学自动驾驶专业项目的博客。GYM-Box2D CarRacing 是一种在 OpenAI Gym 平台上开发和比较强化学习算法的模拟环境。它是流行的 Box2D 物理引擎的一个版本,经过修改以支持模拟汽车在赛道上行驶的物理过程。模块化组件 (Modular Pipeline) 分为 低层次感知与场景解析、路径训练 和车辆控制,本章我们要讲解的内容是 路径训练 (Path training) 部分。
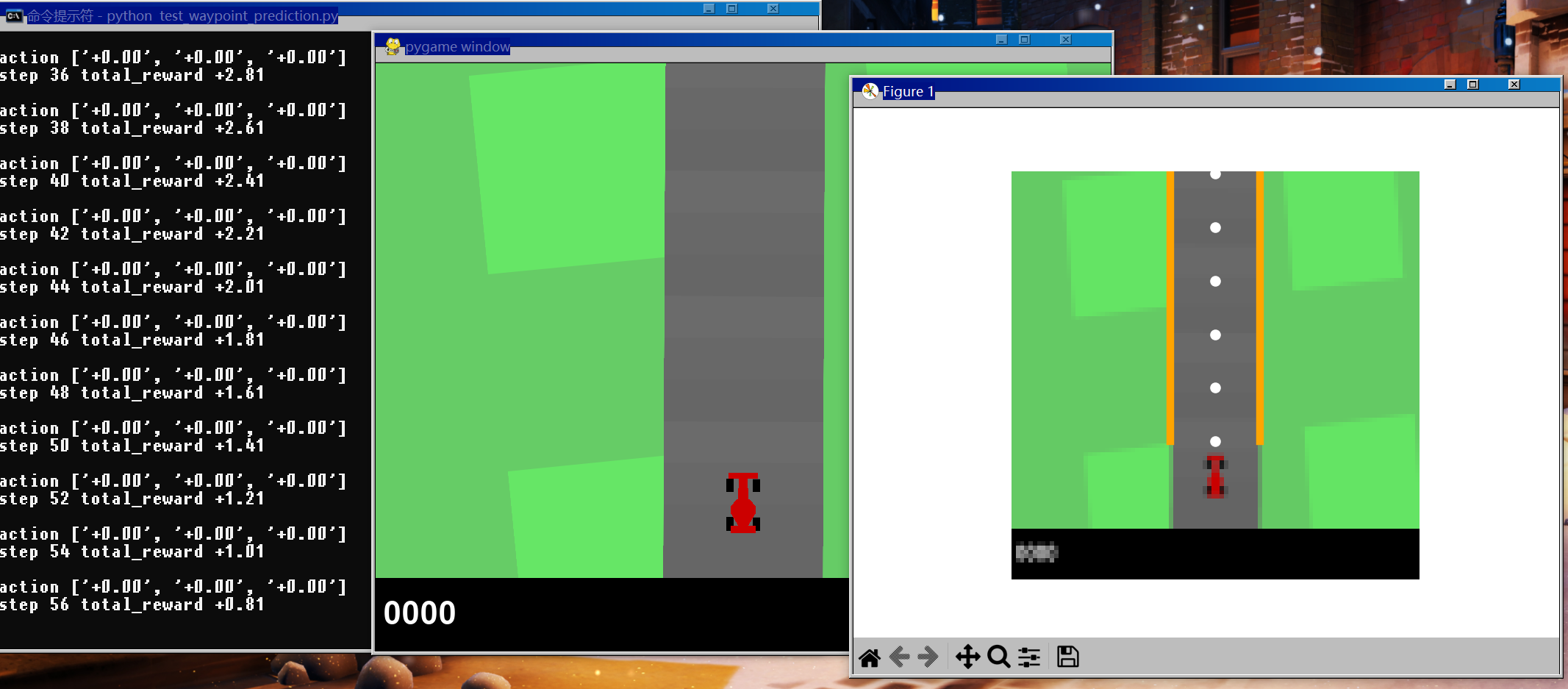
🔗 多伦多大学自动驾驶专项课程:Motion Planning for Self-Driving Cars | Coursera
🔗 Gym Car Racing 文档:Car Racing - Gym Documentation
Ⅰ. 前置知识(Antecedent)
0x00 规划与决策
问题
- ➢ 目标:寻找并遵循一条从这里到目的地的路径(需要考虑静态基础设施和动态物体)
- ➢ 输入:车辆和感知的周围环境状态
- ➢ 输出:将路径或轨迹解析给车辆控制器
难点
- ➢ 驾驶情况和行为是非常复杂的
- ➢ 因此很难将其作为一个单一的优化问题来建模
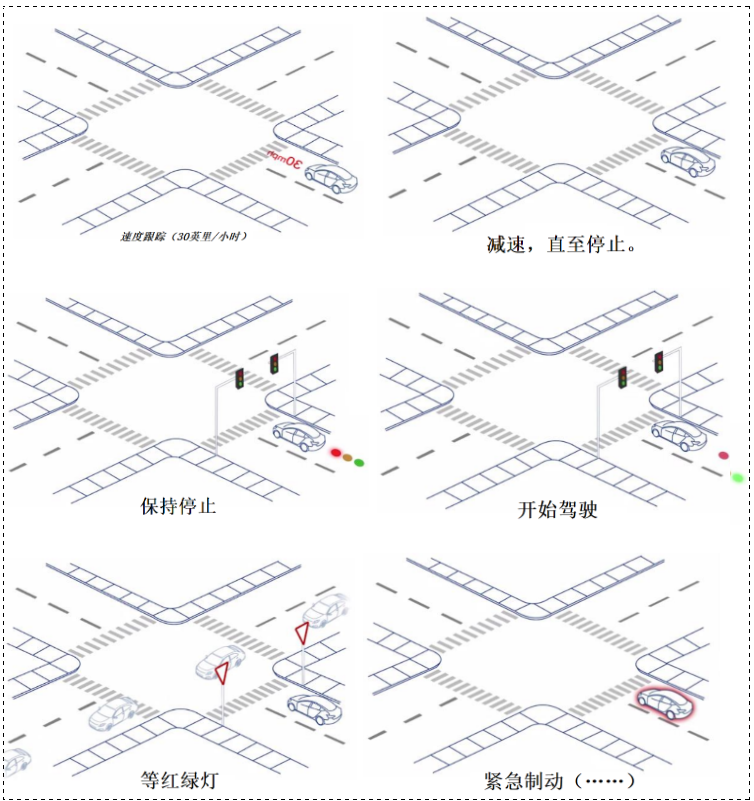
然而要考虑的东西可远不止这些……
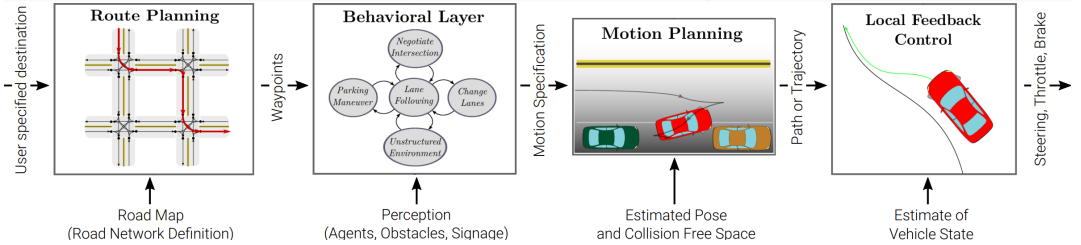
💡 思路:
- 将规划问题分解成更简单的问题的层次结构。
- 每个问题都根据其范围和抽象程度进行调整。
- 在这个层次结构中,越前意味着抽象程度越高。
- 每个优化问题都会有约束条件和目标函数。
路线规划:通过道路网络的路线。
行为层面:响应环境的运动规范。
运动规划:解决一个完成规范的可行路径。
反馈控制:调整执行变量以纠正执行路径中的错误。
0x01 路径规划(Route Planning)
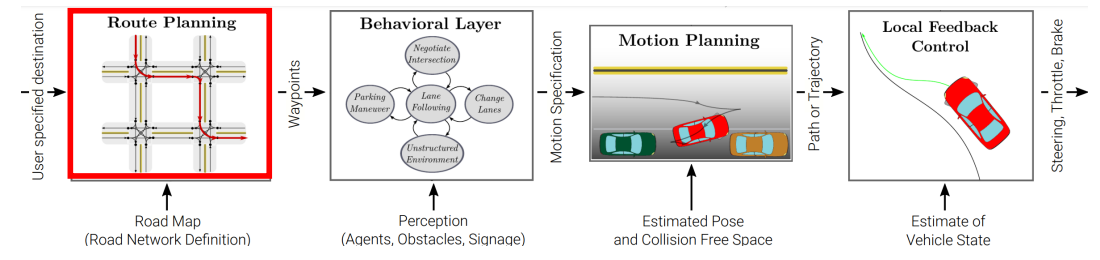
- 以有向图表示道路网络
- 边缘权重对应于路段长度或旅行时间
- 问题转化为一个最小成本的图网络问题
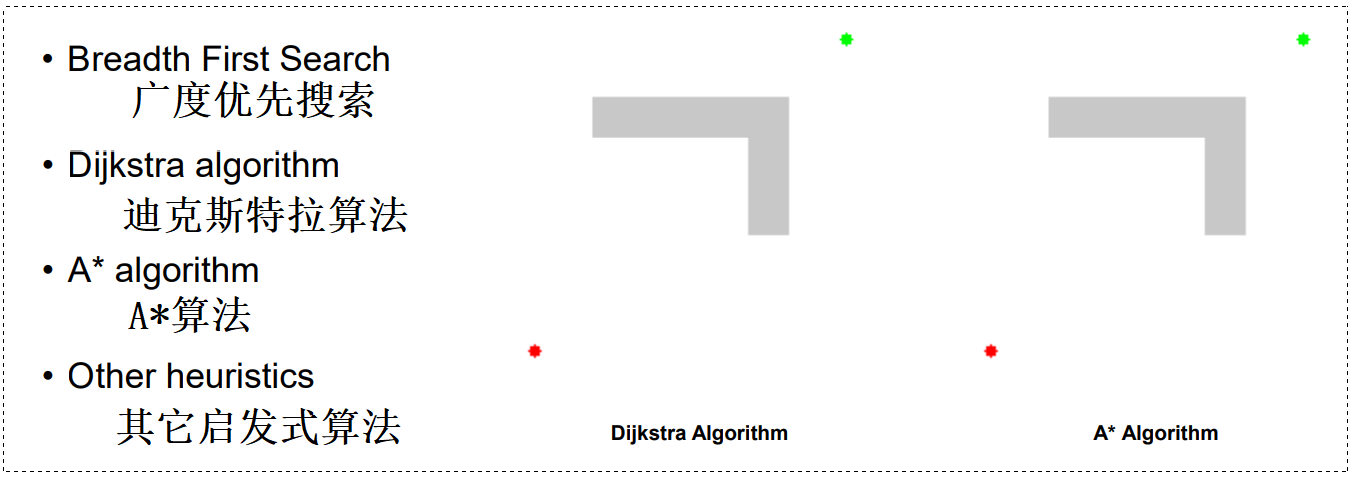
- 推理算法:狄克斯特拉算法,A∗ 算法,……
0x02 行为层(Behavioral Layer)
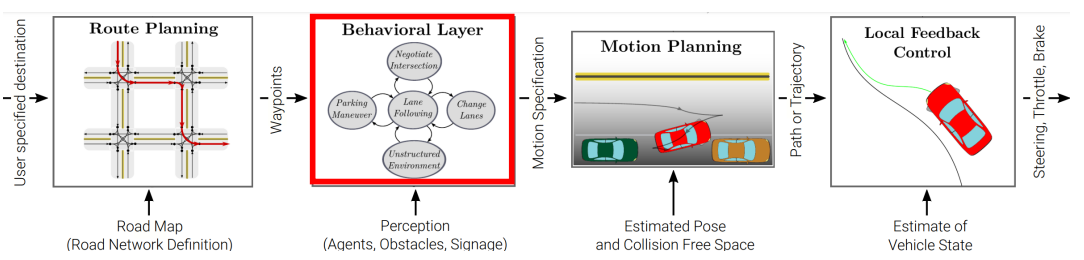
根据当前车辆 / 环境状态选择驾驶行为。
例如,在停车线:停车,观察其他交通参与者,穿行。
通常通过有限状态机进行建模(过渡由感知控制)。
可以通过概率建模,例如使用马尔科夫决策过程(MDPs)。
运动规划:
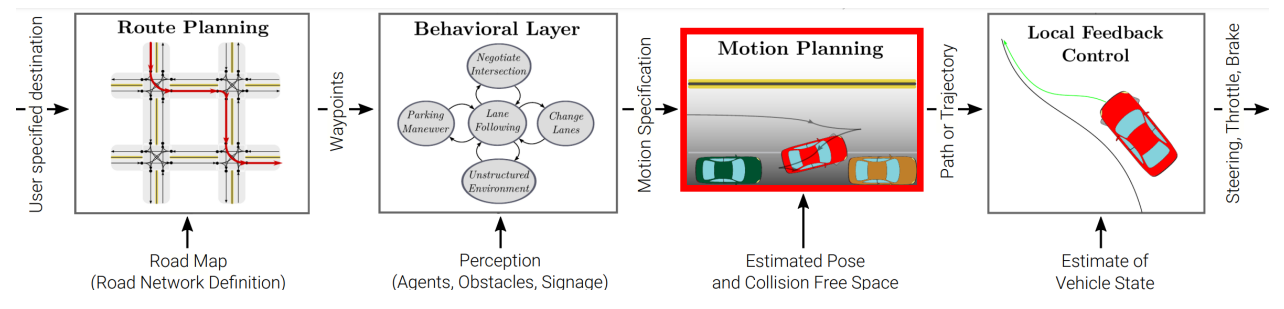
找到可行、舒适、安全和快速的车辆路径 / 轨迹。
在大多数情况下,精确解在计算上难以处理。因此,通常使用数值近似。
方法:变分法、图搜索、基于增量树 。
本地反馈控制:
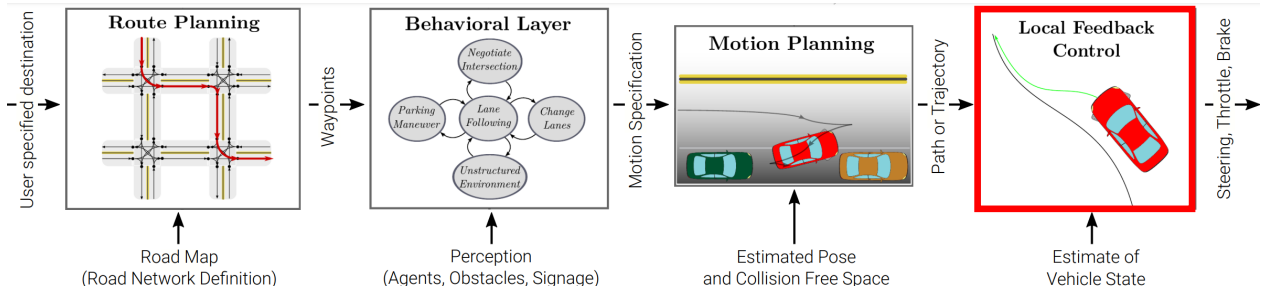
反馈控制器执行来自运动规划器的 路径 / 轨迹
修正了因车辆模型不准确而产生的错误
注重耐用性、稳定性和舒适性
车辆动力学与控制
路径算法:
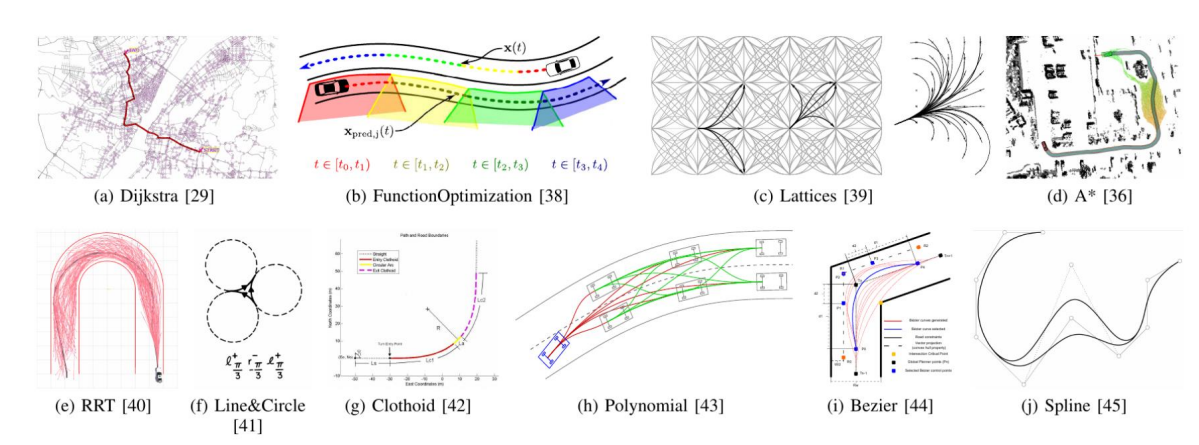
自动驾驶文献中使用的规划算法有很多,本章我们只关注其中的几个即可。
道路网络图:
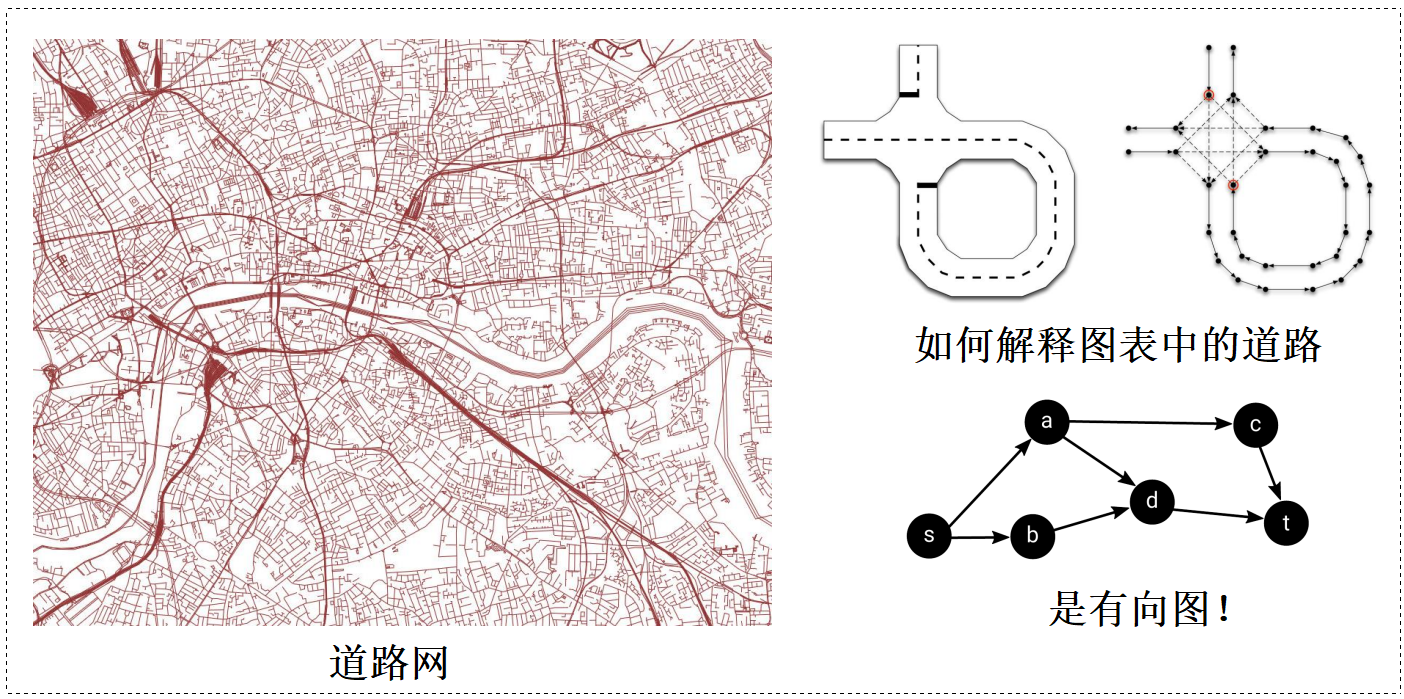
路径规划算法:
0x03 行为规划(Behavior Planning)
简单车辆行为的有限状态机:在驾驶过程中,汽车需要各种机动动作(减速、停车、沿车道行驶等)。将汽车行为离散化为原子机动,开发人员为每个机动设计一个运动规划器。
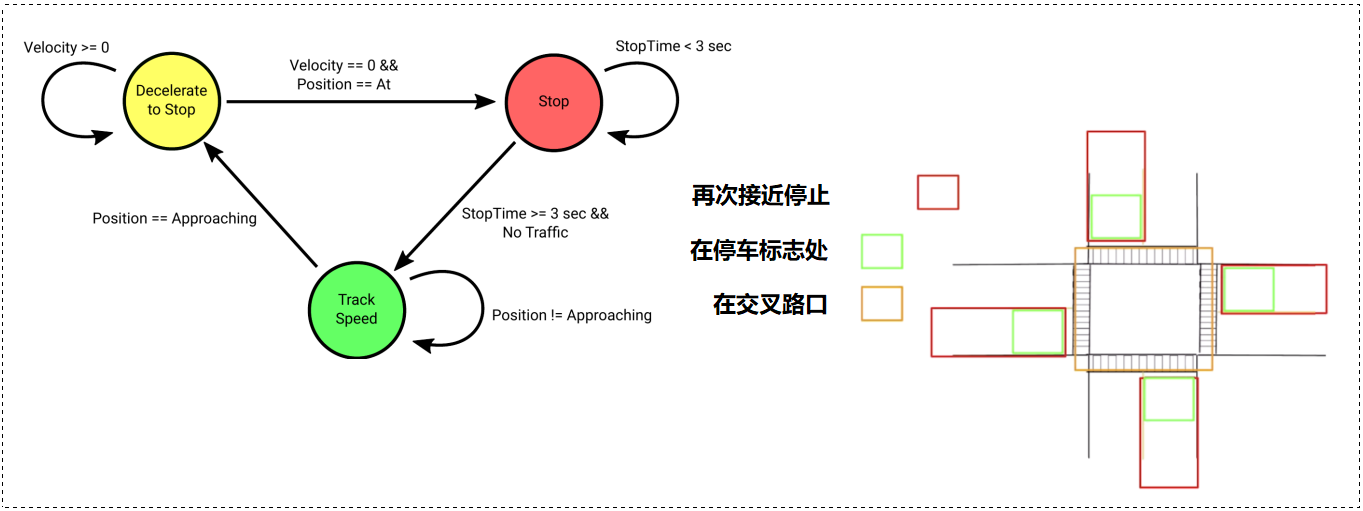
处理多种情况:
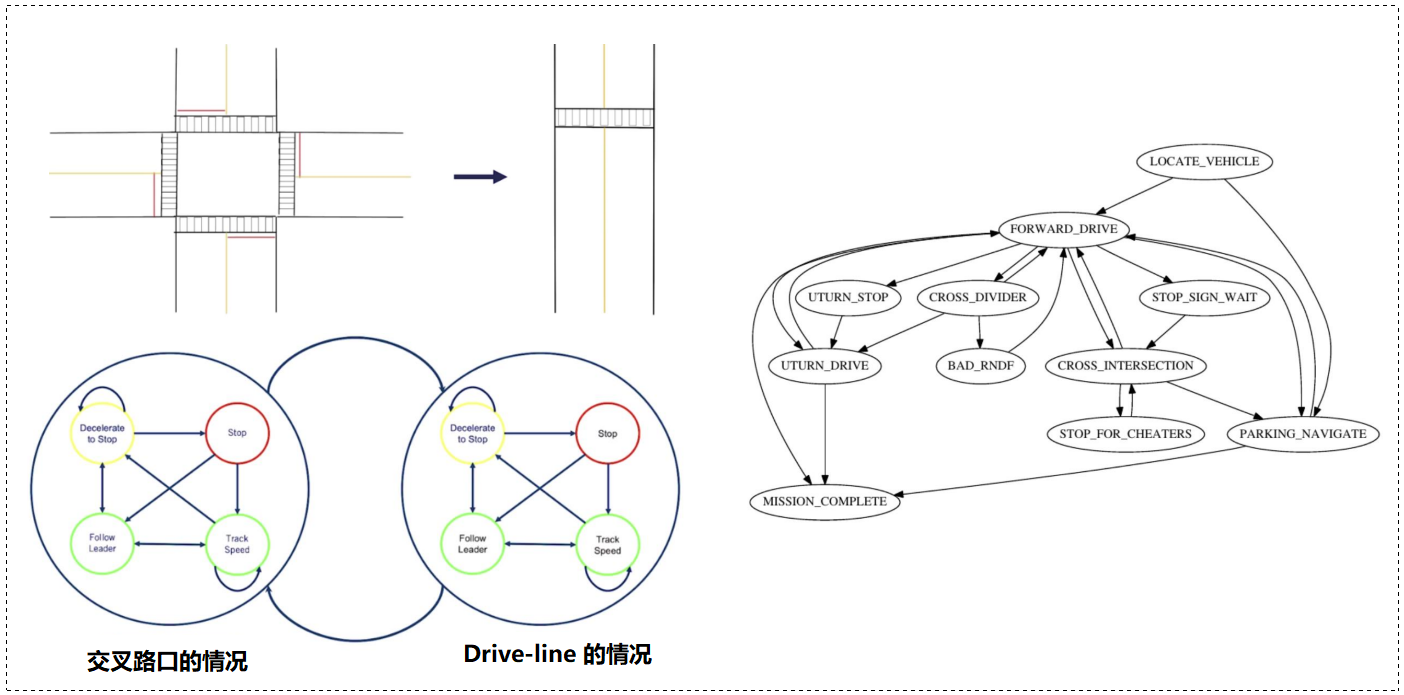
0x04 运动规划(Motion Planning)
变分优化分析(Variational Optimization):变分法最小化一个函数(以一个函数作为输入函数):

变分优化的例子:
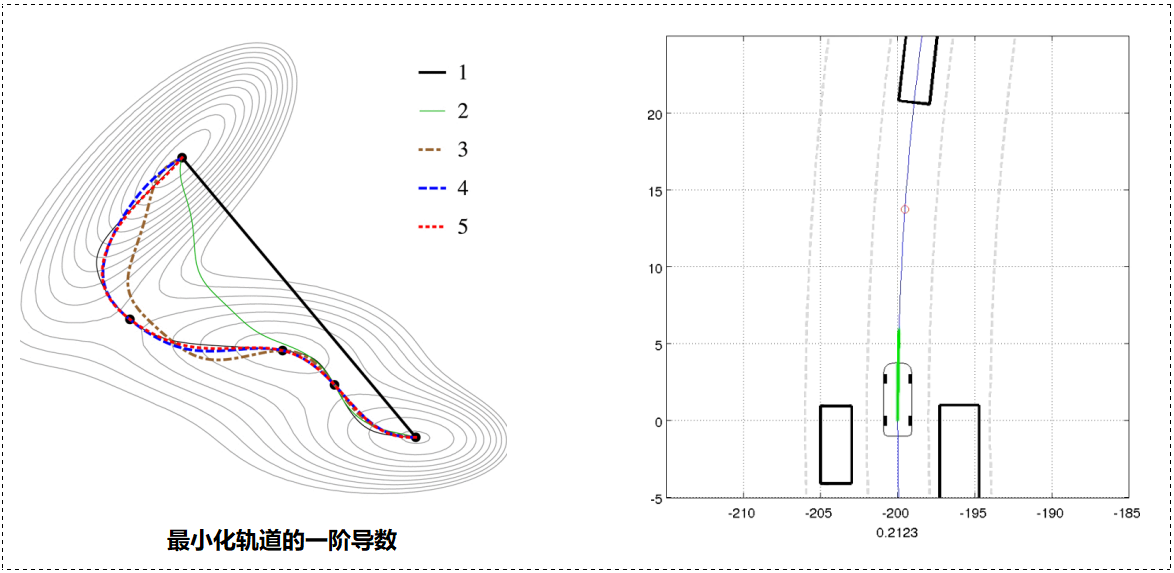
图形搜索方法:将动作空间离散化以绕过变分优化
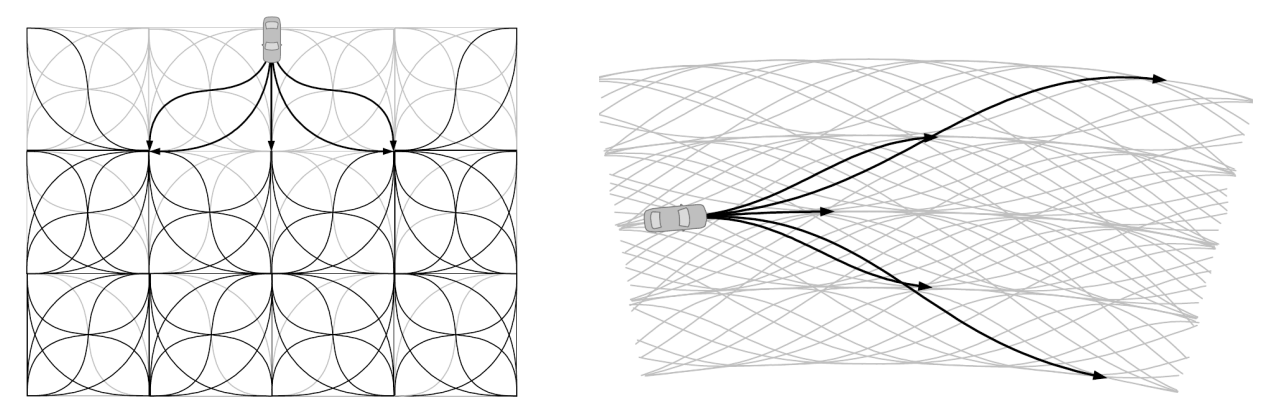
增量搜索技术(Incremental Search Techniques):
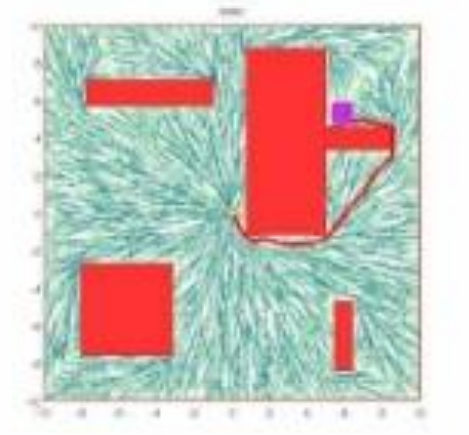 逐步建立配置空间的越来越细的离散化。
逐步建立配置空间的越来越细的离散化。
快速探索随机树(RRT)和 RRT* 算法。
RRT 符合 A* 的算法:
Ⅱ. 实验说明(Experiment)
0x00 模板提供
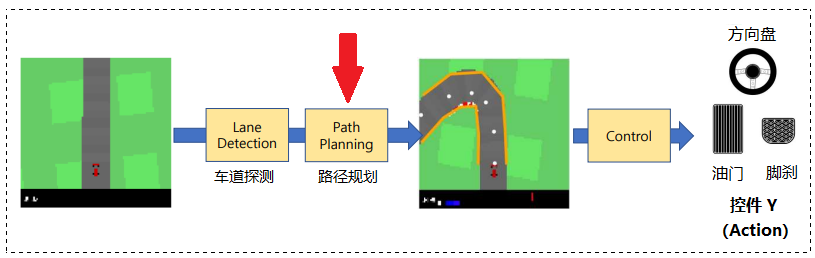
实现模块化管道的简化版本,了解基本概念并获得开发简单自动驾驶应用程序的经验。
📃 提供模板:
1. waypoint_prediction.py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.signal import find_peaks
from scipy.interpolate import splprep, splev
from scipy.optimize import minimize
import time
import sysdef normalize(v):norm = np.linalg.norm(v,axis=0) + 0.00001return v / norm.reshape(1, v.shape[1])def curvature(waypoints):'''##### TODO #####Curvature as the sum of the normalized dot product between the way elementsImplement second term of the smoothin objective.args: waypoints [2, num_waypoints] !!!!!''''''Example)norm_diff = normalize(arguments)norm_diff.shape : (2, num_waypoints)curvature example:3.9999937500073246'''return curvaturedef smoothing_objective(waypoints, waypoints_center, weight_curvature=40):'''Objective for path smoothingargs:waypoints [2 * num_waypoints] !!!!!waypoints_center [2 * num_waypoints] !!!!!weight_curvature (default=40)'''# mean least square error between waypoint and way point centerls_tocenter = np.mean((waypoints_center - waypoints)**2)# derive curvaturecurv = curvature(waypoints.reshape(2,-1))return -1 * weight_curvature * curv + ls_tocenterdef waypoint_prediction(roadside1_spline, roadside2_spline, num_waypoints=6, way_type = "smooth"):'''##### TODO #####Predict waypoint via two different methods:- center- smooth args:roadside1_splineroadside2_splinenum_waypoints (default=6)parameter_bound_waypoints (default=1)waytype (default="smoothed")'''if way_type == "center":##### TODO ###### create spline arguments'''Example)t = np.linspace(arguments)t.shape : (num_waypoints,)'''# derive roadside points from spline'''Example)roadside1_points = np.array(splev(arguments))roadside2_points = np.array(splev(arguments))roadside1_points.shape : (2, num_waypoints)roadside2_points.shape : (2, num_waypoints)roadside1_points example :array([[37. , 37. , 37. , 37. , 37. , 37. ],[ 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ]])roadside2_points example :array([[58. , 58. , 58. , 58. , 58. , 58. ],[ 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ]])'''# derive center between corresponding roadside points'''Example)way_points = np.array( {derive center between corresponding roadside points} )way_points.shape : (2, num_waypoints)way_points example :array([[47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5],[ 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ]])'''return way_pointselif way_type == "smooth":##### TODO ###### create spline points'''Example)t = np.linspace(arguments)t.shape : (num_waypoints,)'''# roadside points from spline'''Example)roadside1_points = np.array(splev(arguments))roadside2_points = np.array(splev(arguments))roadside1_points.shape : (2, num_waypoints)roadside2_points.shape : (2, num_waypoints)roadside1_points example :array([[37. , 37. , 37. , 37. , 37. , 37. ],[ 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ]])roadside2_points example :array([[58. , 58. , 58. , 58. , 58. , 58. ],[ 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ]])'''# center between corresponding roadside points'''Example)way_points_center = (np.array( {derive center between corresponding roadside points} )).reshape(-1)way_points_center.shape : (num_waypoints*2,)way_points_center example :array([47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ])'''# optimization'''scipy.optimize.minimize Doc.)https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.optimize.minimize.htmlExample)way_points = minimize(arguments)way_points.shape : (num_way_points*2,)way_points example :array([47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ])'''return way_points.reshape(2,-1)def target_speed_prediction(waypoints, num_waypoints_used=5,max_speed=60, exp_constant=4.5, offset_speed=30):'''##### TODO #####Predict target speed given waypointsImplement the function using curvature()args:waypoints [2,num_waypoints] for curv_centernum_waypoints_used (default=5) for curv_centermax_speed (default=60) for target_speedexp_constant (default=4.5) for target_speedoffset_speed (default=30) for target_speedoutput:target_speed (float)''''''Example)curv_center = ~~~target_speed = ~~~'''return target_speed2. Test_waypoint_prediction.py (用于测试)
import gym
from gym.envs.box2d.car_racing import CarRacingfrom lane_detection import LaneDetection
from waypoint_prediction import waypoint_prediction, target_speed_prediction
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pyglet
from pyglet import gl
from pyglet.window import key
import pygame# action variables
action = np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
def register_input():for event in pygame.event.get():if event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN:if event.key == pygame.K_LEFT:action[0] = -1.0if event.key == pygame.K_RIGHT:action[0] = +1.0if event.key == pygame.K_UP:action[1] = +0.5if event.key == pygame.K_DOWN:action[2] = +0.8 # set 1.0 for wheels to block to zero rotationif event.key == pygame.K_r:global retryretry = Trueif event.key == pygame.K_s:global recordrecord = Trueif event.key == pygame.K_q:global quitquit = Trueif event.type == pygame.KEYUP:if event.key == pygame.K_LEFT and action[0] < 0.0:action[0] = 0if event.key == pygame.K_RIGHT and action[0] > 0.0:action[0] = 0if event.key == pygame.K_UP:action[1] = 0if event.key == pygame.K_DOWN:action[2] = 0# init environement
env = CarRacing()
env.render()
env.reset()# define variables
total_reward = 0.0
steps = 0
restart = False# init modules of the pipeline
LD_module = LaneDetection()# init extra plot
fig = plt.figure()
plt.ion()
plt.show()while True:# perform stepregister_input()s, r, done, speed = env.step(action)# lane detectionlane1, lane2 = LD_module.lane_detection(s)# waypoint and target_speed predictionwaypoints = waypoint_prediction(lane1, lane2)target_speed = target_speed_prediction(waypoints)# rewardtotal_reward += r# outputs during trainingif steps % 2 == 0 or done:print("\naction " + str(["{:+0.2f}".format(x) for x in action]))print("step {} total_reward {:+0.2f}".format(steps, total_reward))LD_module.plot_state_lane(s, steps, fig, waypoints=waypoints)steps += 1env.render()# check if stopif done or restart or steps>=600: print("step {} total_reward {:+0.2f}".format(steps, total_reward))breakenv.close()0x01 道路中心(Road Center)
汽车的一个简单路径是沿着道路中心行驶,使用车道边界样条曲线,导出 6 个等距样条曲线参数值的车道边界点。
→ waypoint_prediction()
使用相同样条曲线参数确定车道边界点之间的中心
→ waypoint_prediction()
0x02 路径平滑(Path Smoothing)
由于我们正在创建一辆赛车,我们需要根据道路的走向来调整航点,例如打到顶点。我们通过最小化以下方程来做到这一点。在给定中心航路点 的情况下,通过最小化以下关于航路点
的目标来改善路径。
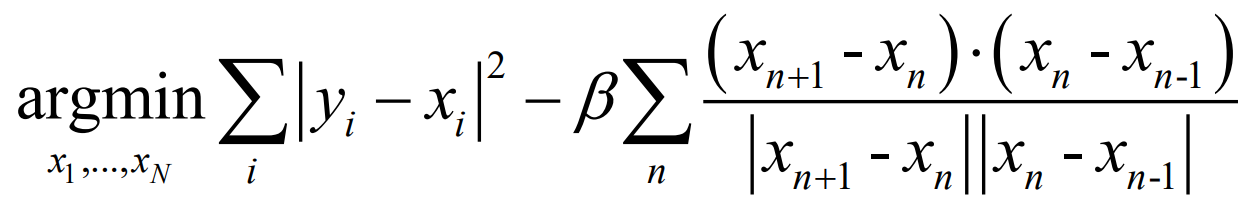
解释第二项的效果,并实施第二项。
其中, 是为了最小化目标而变化的航点,
是任务中估计的中心航点。
→ curvature()
0x03 目标速度预测(Target Speed Prediction)
除了空间路径外,我们还需要知道汽车在路径上应该开多快。从启发式的角度来看,如果路径是平滑的,汽车应该加速到最大速度,并在转弯前减速。实现一个函数,输出状态图像中预测路径的目标速度,参考如下公式:
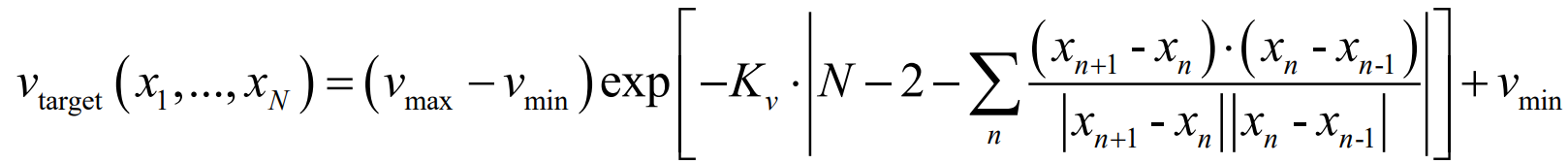
* 初始参数采用:
→ target_speed_prediction()
Ⅲ. 代码实现
0x00 curvature 函数
💬 提供的基础模板如下:
def curvature(waypoints):'''##### TODO #####Curvature as the sum of the normalized dot product between the way elementsImplement second term of the smoothin objective.args: waypoints [2, num_waypoints] !!!!!''''''Example)norm_diff = normalize(arguments)norm_diff.shape : (2, num_waypoints)curvature example:3.9999937500073246'''return curvature根据提示可知,该部分属于计算路径曲率。曲率作为路元素之间的归一化点积之和,实现平滑目标的第二项。根据提示,输入的是一个二维数组,其中每一列代表路径中的一个点。
首先定义出 curv,我们可以从第二个点开始遍历到倒数第二个点,计算每个点的曲率。
curv = 0
for p in range(1, waypoints.shape[1] - 1):...创建数组,分别记录当前点、上一个点和下一个点:
x = np.array(waypoints[:, p])y = np.array(waypoints[:, p + 1])z = np.array(waypoints[:, p - 1])这里可以使用 reshape 函数,reshape() 函数的功能是改变数组或矩阵的形状,并将这些数组改为一个2行的二维新数组。
px, py, pz = x.reshape(N, AUTO_CALC), y.reshape(N, AUTO_CALC), z.reshape(N, AUTO_CALC)
然后可以使用 np.dot() 返回两个数组的点积:
matrixA = normalize(px - pz)matrixB = normalize(py - px)matrixB_T = matrixB.transpose() # .transpose() == .Tdot_product = np.dot(matrixB_T, matrixA)最后再利用 flatten() 将结果降维,最后返回 curv 即可。
curv += dot_product.flatten()return curv0x01 smoothing_objective 函数
def smoothing_objective(waypoints, waypoints_center, weight_curvature=40):'''Objective for path smoothingargs:waypoints [2 * num_waypoints] !!!!!waypoints_center [2 * num_waypoints] !!!!!weight_curvature (default=40)'''# mean least square error between waypoint and way point centerls_tocenter = np.mean((waypoints_center - waypoints)**2)# derive curvaturecurv = curvature(waypoints.reshape(2,-1))return -1 * weight_curvature * curv + ls_tocenterls_tocenter = np.mean((waypoints_center - waypoints.reshape(2, -1))**2)
0x02 waypoint_prediction 函数
def waypoint_prediction(roadside1_spline, roadside2_spline, num_waypoints=6, way_type = "smooth"):'''##### TODO #####Predict waypoint via two different methods:- center- smooth args:roadside1_splineroadside2_splinenum_waypoints (default=6)parameter_bound_waypoints (default=1)waytype (default="smoothed")'''if way_type == "center":##### TODO ###### create spline arguments'''Example)t = np.linspace(arguments)t.shape : (num_waypoints,)'''num_waypoints_default = 6parameter_bound_waypoints_default = 1# 利用 linsapce() 创建等差数列AP = np.linspace( 0, parameter_bound_waypoints_default, num_waypoints_default)way_points = np.zeros((N, num_waypoints))# derive roadside points from spline'''Example)roadside1_points = np.array(splev(arguments))roadside2_points = np.array(splev(arguments))roadside1_points.shape : (2, num_waypoints)roadside2_points.shape : (2, num_waypoints)roadside1_points example :array([[37. , 37. , 37. , 37. , 37. , 37. ],[ 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ]])roadside2_points example :array([[58. , 58. , 58. , 58. , 58. , 58. ],[ 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ]])'''# 中间点可视化: B样条和它的导数插值# display1, display2 = splev(AP, roadside1_spline), splev(AP, roadside2_spline)# p1 = np.array(display1)# p2 = np.array(display2)p1 = np.array(splev(AP, roadside1_spline))p2 = np.array(splev(AP, roadside2_spline))# derive center between corresponding roadside points'''Example)way_points = np.array( {derive center between corresponding roadside points} )way_points.shape : (2, num_waypoints)way_points example :array([[47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5],[ 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ]])'''p1_sp, p2_sp = p1.shape[1], p2.shape[1]for i in range( min(p1_sp, p2_sp) ):way_points[:, i] = np.array( (p1[:, i] + p2[:, i]) / 2) # 求中点return way_pointselif way_type == "smooth":##### TODO ###### create spline points'''Example)t = np.linspace(arguments)t.shape : (num_waypoints,)''' # roadside points from spline'''Example)roadside1_points = np.array(splev(arguments))roadside2_points = np.array(splev(arguments))roadside1_points.shape : (2, num_waypoints)roadside2_points.shape : (2, num_waypoints)roadside1_points example :array([[37. , 37. , 37. , 37. , 37. , 37. ],[ 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ]])roadside2_points example :array([[58. , 58. , 58. , 58. , 58. , 58. ],[ 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ]])'''# center between corresponding roadside points'''Example)way_points_center = (np.array( {derive center between corresponding roadside points} )).reshape(-1)way_points_center.shape : (num_waypoints*2,)way_points_center example :array([47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ])'''way_points_center = waypoint_prediction(roadside1_spline, roadside2_spline, way_type = "center")# optimization'''scipy.optimize.minimize Doc.)https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.optimize.minimize.htmlExample)way_points = minimize(arguments)way_points.shape : (num_way_points*2,)way_points example :array([47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ])'''# 利用 minimize 进行非线性优化 # minimize(func, xo, args, **pos) # func:优化目标 # xo:优化参数初始值 # args:优化目标中其他参数的值way_points = minimize (smoothing_objective,(way_points_center),args = way_points_center)["x"]return way_points.reshape(2,-1)0x03 target_speed_prediction 函数
提供的模板如下:
def target_speed_prediction(waypoints, num_waypoints_used=5,max_speed=60, exp_constant=4.5, offset_speed=30):'''##### TODO #####Predict target speed given waypointsImplement the function using curvature()args:waypoints [2,num_waypoints] for curv_centernum_waypoints_used (default=5) for curv_centermax_speed (default=60) for target_speedexp_constant (default=4.5) for target_speedoffset_speed (default=30) for target_speedoutput:target_speed (float)''''''Example)curv_center = ~~~target_speed = ~~~'''return target_speed这里只需要将提供的公式写成代码形式即可,最后将结果返回。
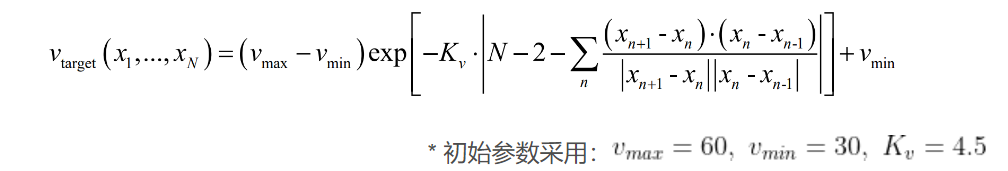
Vmax = max_speedVmin = offset_speedKv = exp_constantN = num_waypoints_usedE = curvature(waypoints)# Path Planning 公式Vtarget = (Vmax - Vmin) * math.exp( -Kv * abs(N - 2 - E) ) + Vmin0x04 运行结果演示
cd 到 skeleton 文件夹的路径下,输入 python test_lane_detection 运行代码:

🚩 运行结果如下:


📌 [ 笔者 ] 王亦优
📃 [ 更新 ] 2023.2.23
❌ [ 勘误 ] /* 暂无 */
📜 [ 声明 ] 由于作者水平有限,本文有错误和不准确之处在所难免,本人也很想知道这些错误,恳望读者批评指正!| 📜 参考资料 [6] Montemerlo M, Becker J, Bhat S, et al. Junior: The Stanford entry in the Urban Challenge Slide Credit: Steven Waslander Course 自动驾驶课程:Motion Planning for Self-Driving Cars | Coursera LaValle: Rapidly-exploring random trees: A new tool for path planning. Techical Report, 1998 Dolgov et al.: Practical Search Techniques in Path Planning for Autonomous Driving. STAIR, 2008. Microsoft. MSDN(Microsoft Developer Network)[EB/OL]. []. . 百度百科[EB/OL]. []. https://baike.baidu.com/. . [EB/OL]. []. https://blog.waymo.com/2021/10/the-waymo-driver-handbook-perception.html. |
