赶集网站建设多少钱墨子学院seo
目录
前言:
1.概念
链表定义
结点结构体定义
结点的创建
2.链表的头插法
动画演示
代码实现
3.链表的尾插
动画演示
代码实现
4.链表的头删
动画演示
代码实现
5.链表的尾删
动画演示
代码实现
6.链表从中间插入结点
动画演示
代码实现
7.从单链表中删除任意结点
动画演示
代码实现
8.销毁链表
动画演示
代码实现
完整代码
前言:
前面我们已经把顺序表的优点和缺点讲了,那么这篇文章就是单链表的这种数据结构的实现和理解。
1.概念
链表定义
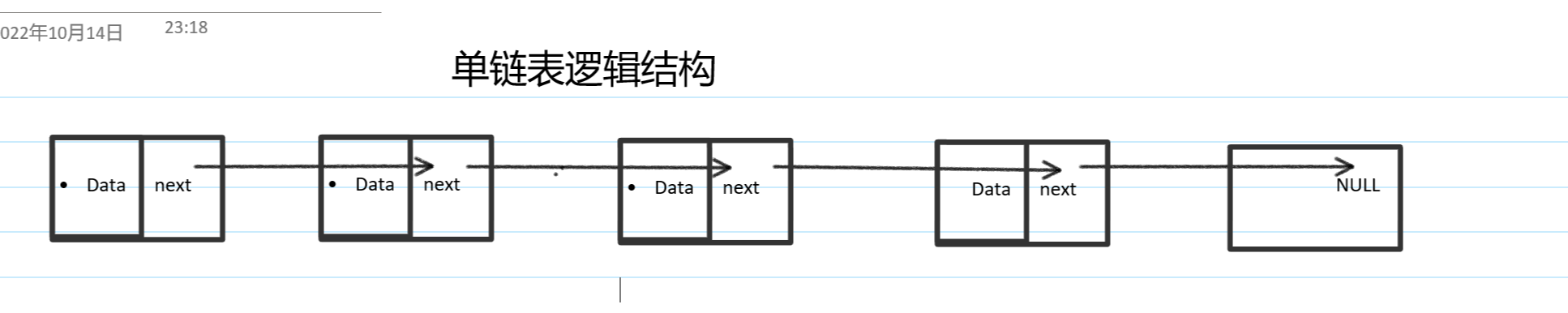
链表是一种离散存储的数据结构,它只有一个指针域,下一个指针保存着前一个数据的地址;像链子一样串起来的结构就叫做单链表。
n个节点离散分配, 彼此通过指针相连每个节点只有一个前驱节点,每个节点只有一个后续节点。首节点没有前驱节点,尾节点没有后续节点。
结点结构体定义
struct ListNode {DataType data; //数据域struct ListNode*next; //指针域
}ListNode;结点的创建
为链表创建新结点并分配内存,把传进来的值赋给data, next置为空指针,并返回新结点。
ListNode *ListCreateNode(DataType data) {ListNode *node = (ListNode *) malloc ( sizeof(ListNode) );if (node == NULL){perror("malloc");exit(-1);}node->data = data;node->next = NULL;return node;
}2.链表的头插法
动画演示
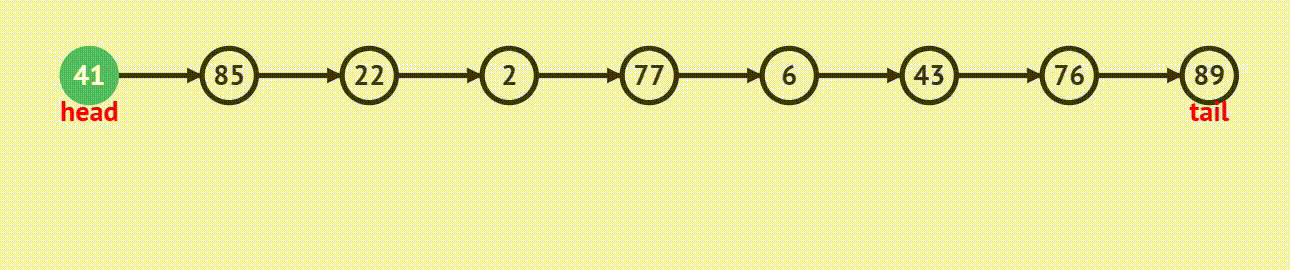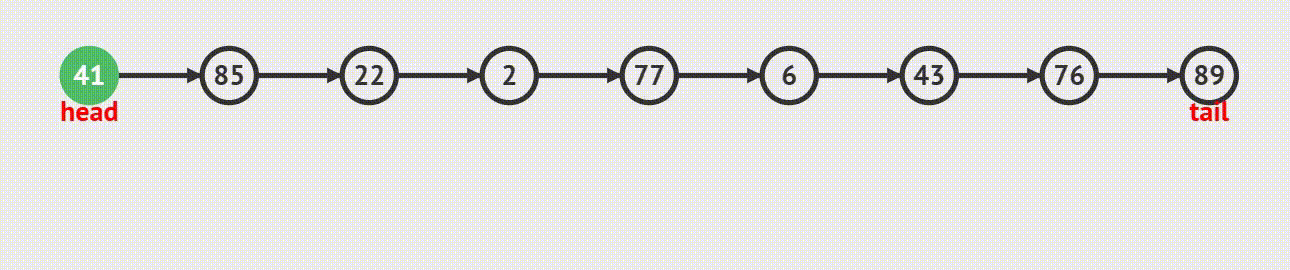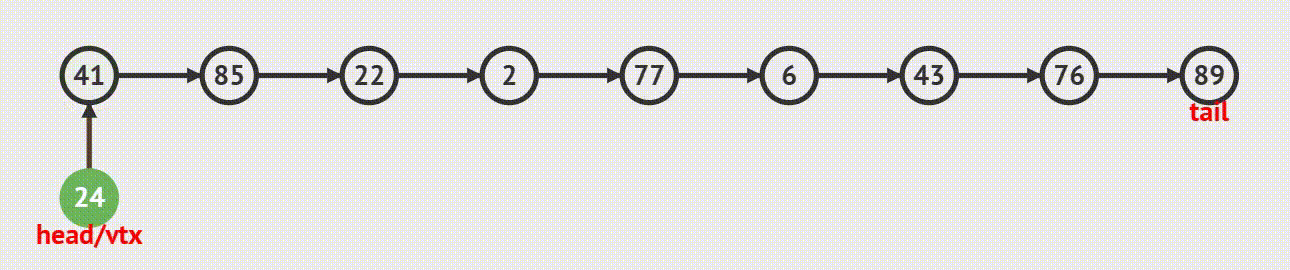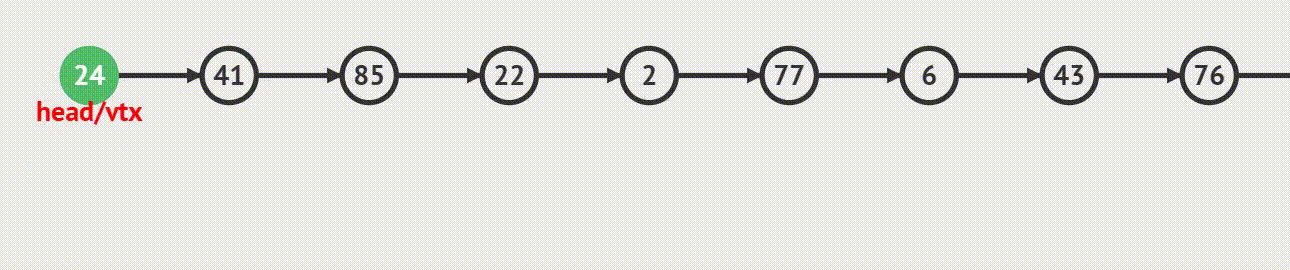
链表的头插有两种情况 : 1.如果链表为空 ,执行头部插入 2.链表不为空,需要找到链表的头再进行插入
情况 1的处理
当前是空链表,插入之后成为头结点。
情况 2
当前链表不为空,则需要找到当前头结点,让新结点指向头结点;头结点再指向新结点。
代码实现
void SListPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);newnode->next = *pphead;*pphead = newnode;
}3.链表的尾插
动画演示
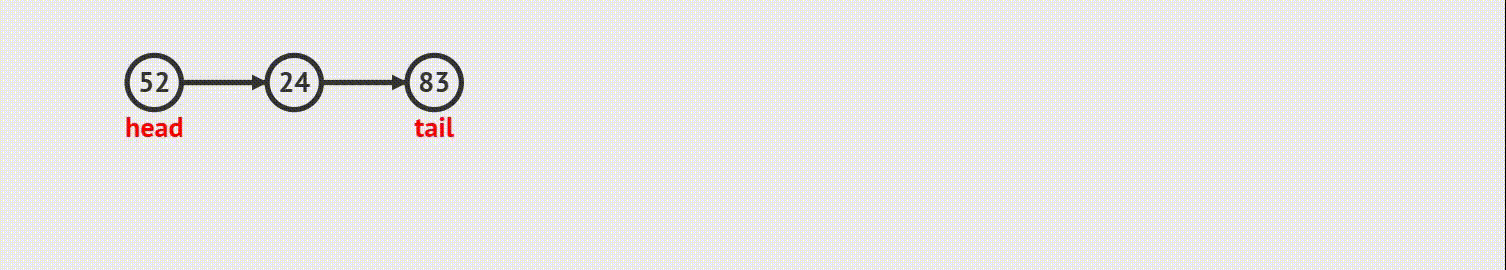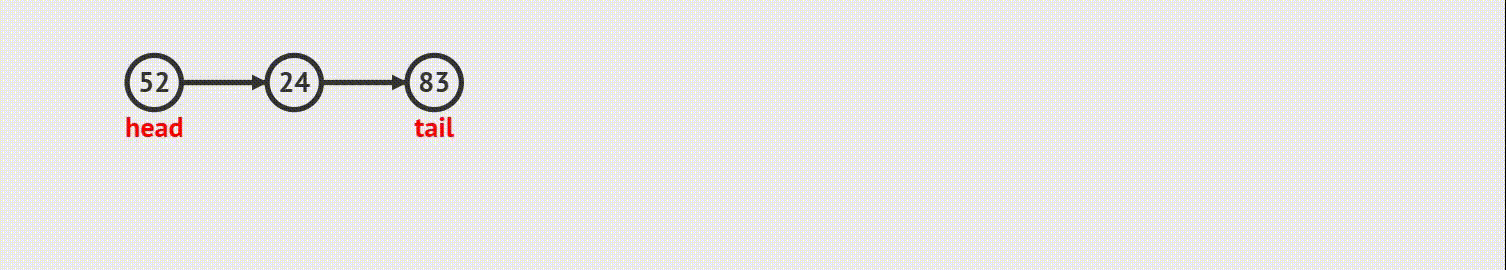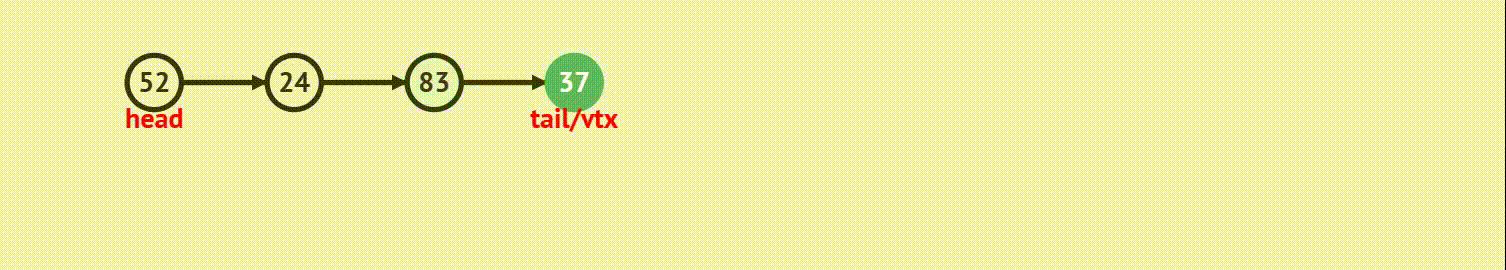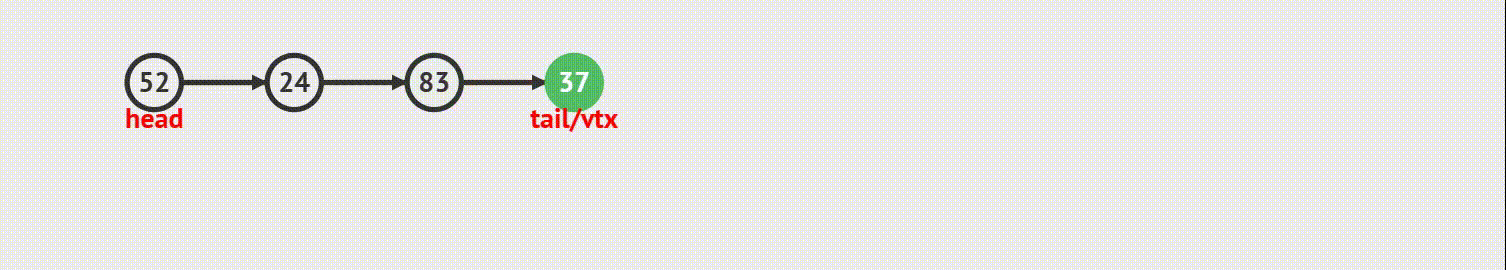
代码实现
1. 如果当前链表为空 ,那么尾插 等于 头插
2. 如果当前链表不为空,则需要找到最后一个结点,让最后一个结点的指针指向新结点,新结点再指向尾结点、
void SListPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);if (*pphead == NULL){*pphead = newnode;}else{// 找尾节点SLTNode* tail = *pphead;while (tail->next != NULL){tail = tail->next;}tail->next = newnode;}
}
4.链表的头删
函数接口
void SListPopFront(SLTNode** pphead)动画演示
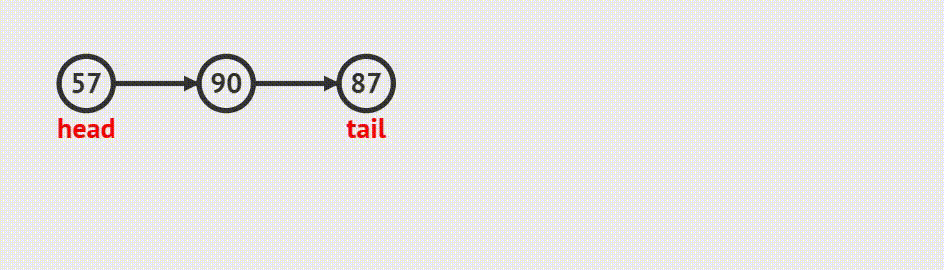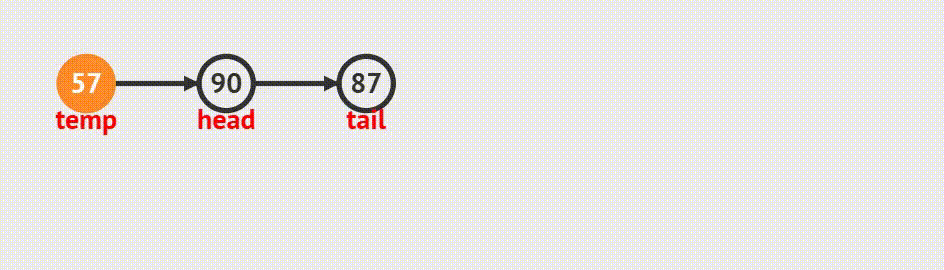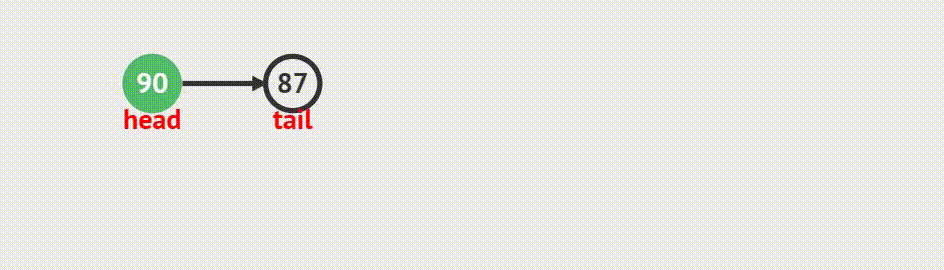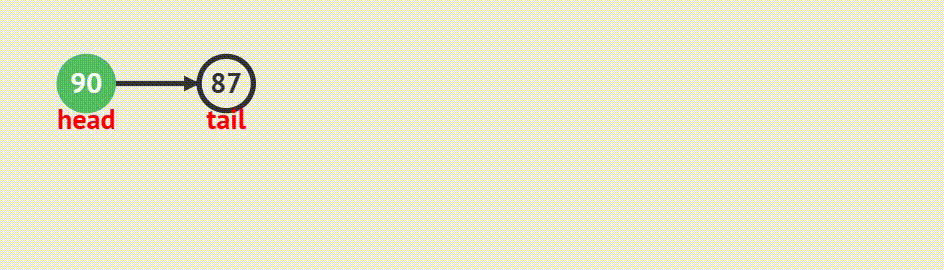
代码实现
1.如果当前链表是空的,不用删
2. 如果当前链表还有结点,则继续删。
void SListPopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
{assert(*pphead != NULL);//if (*pphead == NULL)// return;SLTNode* next = (*pphead)->next;free(*pphead);*pphead = next;
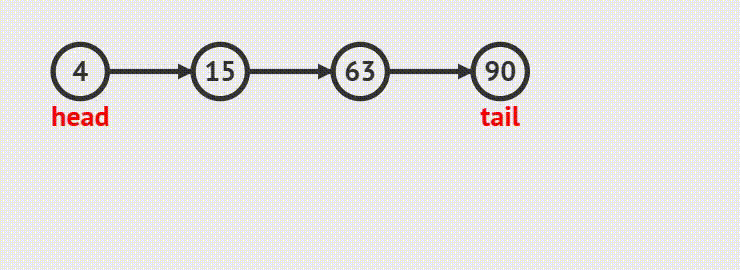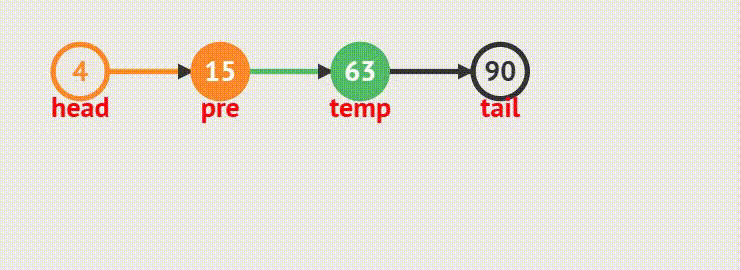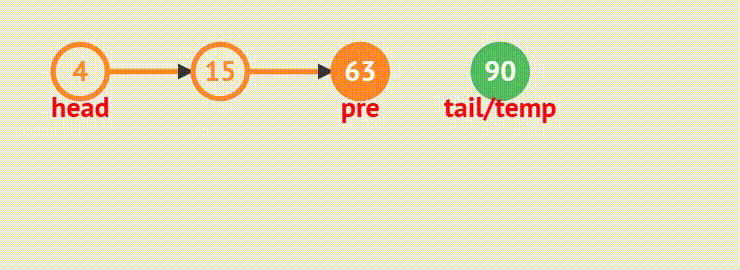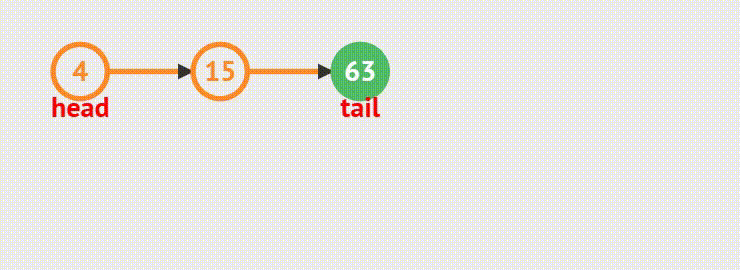
}5.链表的尾删
函数接口:
void SListPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)动画演示
代码实现
1. 链表内只有一个结点的情况,将当前结点的指针置为NULL,再释放当前结点。最后置空
2.如果链表内有多个结点存在,则需要遍历链表找到尾结点,然后释放尾结点;最后将指针置为NULL,防止空指针异常。
void SListPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
{assert(*pphead);// 1、只有一个节点// 2、多个节点if ((*pphead)->next == NULL){free(*pphead);*pphead = NULL;}else{/*SLTNode* tailPrev = NULL;SLTNode* tail = *pphead;while (tail->next != NULL){tailPrev = tail;tail = tail->next;}free(tail);tailPrev->next = NULL;*/SLTNode* tail = *pphead;while (tail->next->next != NULL){tail = tail->next;}free(tail->next);tail->next = NULL;}
}
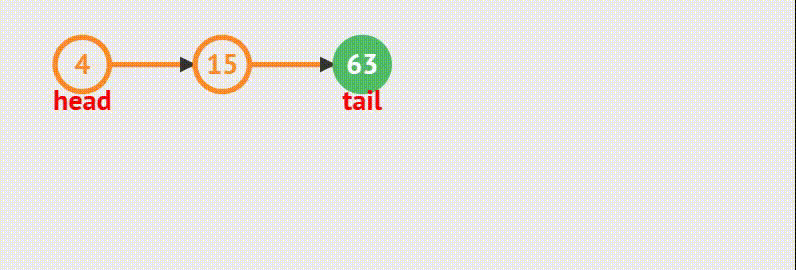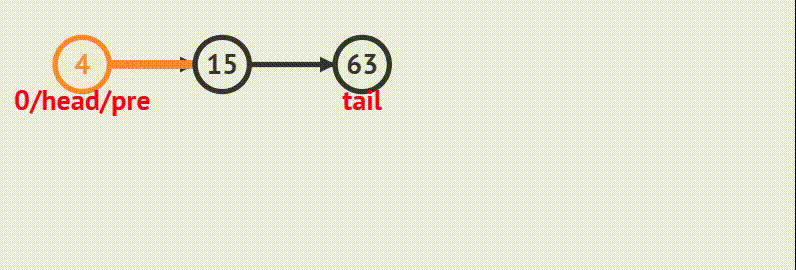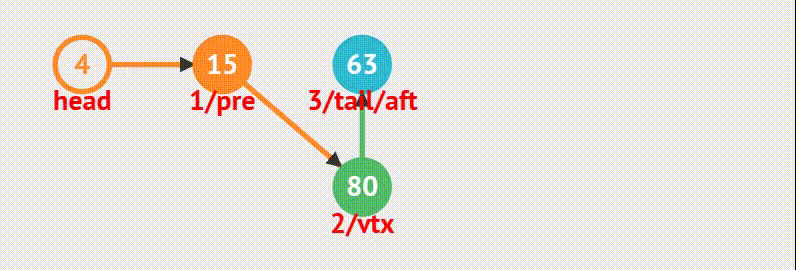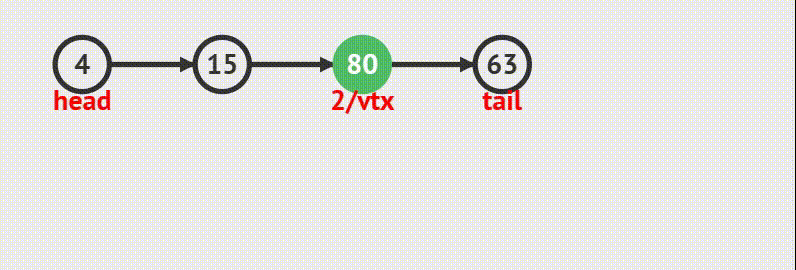
6.链表从中间插入结点
在第 i 个结点后面插入一个数据,数据值为 v
规则说明:
Head 为链表头,并且头结点内有数据
i >= 0
动画演示
代码实现
先分析情况
1.如果当前链表为空,则链表不需要删除。
2.如果链表不为空,则需要让新结点指向要插入的结点,再让前一个结点指向新结点。
ListNode *ListInsertNode(ListNode *head, int i, DataType v) {ListNode *pre, *aft, *vtx; // (1) 插入完毕后, pre -> vtx -> aft int j = 0; // (2) 定义一个计数器,当 j == i 时,表明找到要插入的位置 pre = head; // (3) 从链表头开始while(pre && j < i) { // (4) 如果还没有到链表尾,或者没有找到插入位置则继续循环 pre = pre->next; // (5) 游标指针指向它的后继结点 ++j; // (6) 计数器加 1 }if(!pre) { return NULL; // (7) 元素个数不足,无法找到给定位置,返回 NULL }vtx = ListCreateNode(v); // (8) 创建一个值为 v 的鼓孤立结点 aft = pre->next; // (9) - (11) 为了串成 pre -> vtx -> aft vtx->next = aft; // (10)pre->next = vtx; // (11)return vtx; // (12) 返回插入的那个结点
}
7.从单链表中删除任意结点
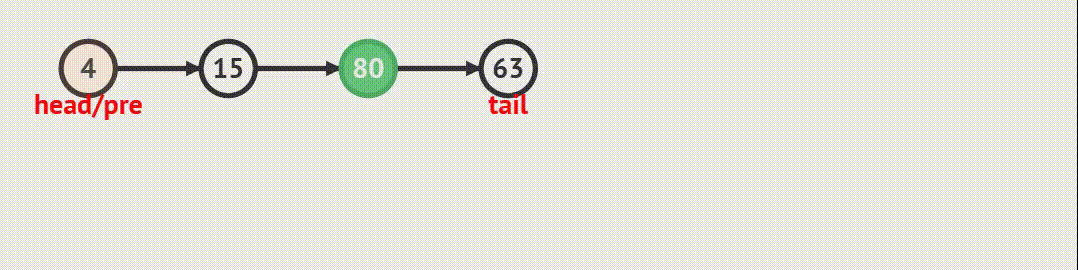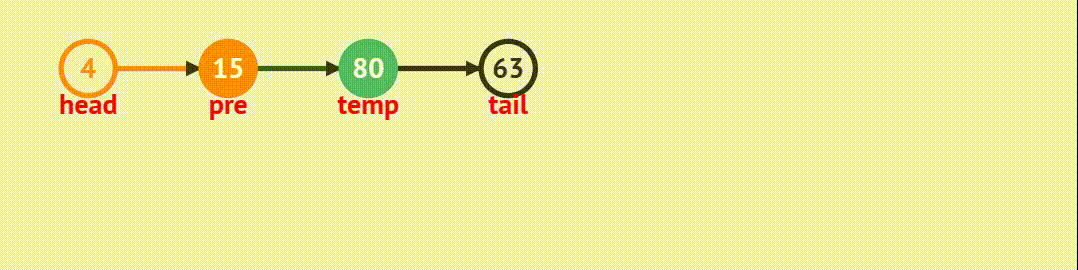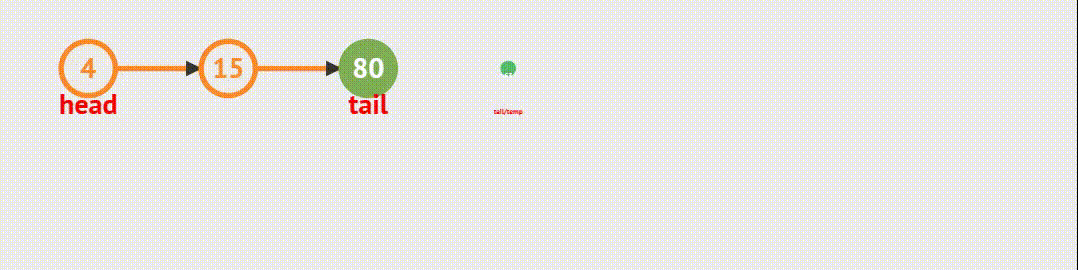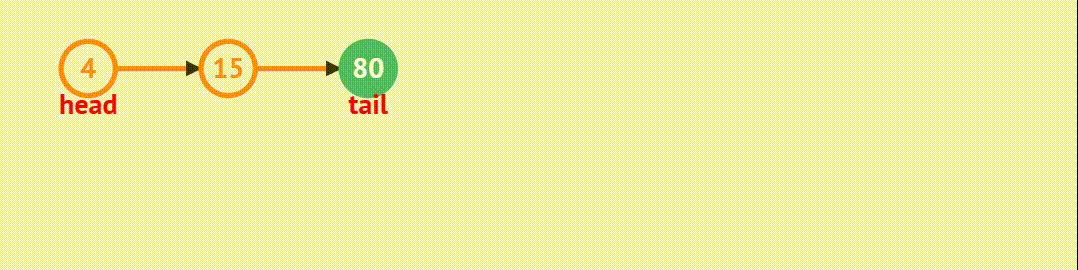
删除任意结点跟任意位置插入结点的思路是一致的,只是反着来。
动画演示
代码实现
分情况讨论
1.如果当前链表为空,不需要删除
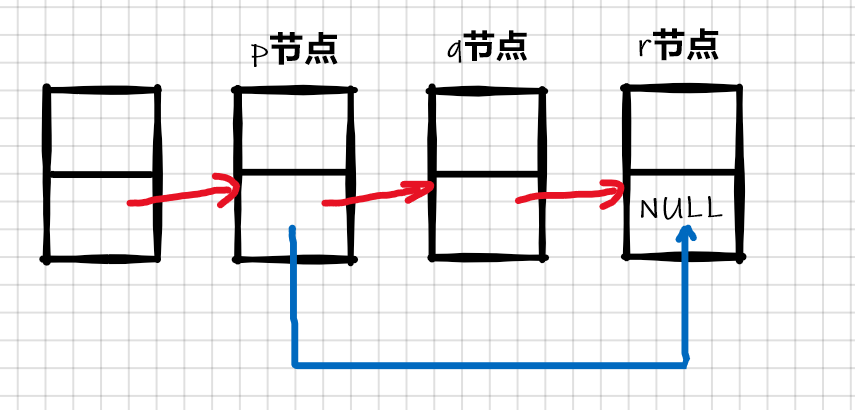
2.不为空,先找到要删除结点的前一个结点,让前一个结点指向要删除的结点的后一个结点,然后释放要删除结点的内存,再让后一个结点的指针指向前一个结点.
void SListErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos)
{assert(pphead);assert(pos);if (*pphead == pos){SListPopFront(pphead);}else{SLTNode* prev = *pphead;while (prev->next != pos){prev = prev->next;}prev->next = pos->next;free(pos);pos = NULL;}
}8.销毁链表
函数接口:
void ListDestroyList(ListNode **pHead)动画演示
代码实现
1.链表为空,不删除。
2.链表不为空,遍历链表释放结点,最后指针置空。
void ListDestroyList(ListNode **pHead) { // (1) 这里必须用二级指针,因为删除后需要将链表头置空,普通传参无法影响外部变量; ListNode *head = *pHead; // (2) 给链表头解引用; while(head) { // (3) 如果链表非空,则继续循环; head = ListDeleteNode(head, 0); // (4) 产出链表头部,并且返回 后继结点; ListPrint(head);}*pHead = NULL; // (5) 将链表头置空
}完整代码
#include "SList.h"void SListPrint(SLTNode* phead)
{SLTNode* cur = phead;while (cur != NULL){printf("%d->", cur->data);cur = cur->next;}printf("NULL\n");
}SLTNode* BuySListNode(SLTDataType x)
{SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));assert(newnode);newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;return newnode;
}void SListPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{assert(pphead);SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);if (*pphead == NULL){*pphead = newnode;}else{// 找尾节点SLTNode* tail = *pphead;while (tail->next != NULL){tail = tail->next;}tail->next = newnode;}
}void SListPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{assert(pphead);SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);newnode->next = *pphead;*pphead = newnode;
}void SListPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
{assert(pphead);assert(*pphead);// 1、只有一个节点// 2、多个节点if ((*pphead)->next == NULL){free(*pphead);*pphead = NULL;}else{/*SLTNode* tailPrev = NULL;SLTNode* tail = *pphead;while (tail->next != NULL){tailPrev = tail;tail = tail->next;}free(tail);tailPrev->next = NULL;*/SLTNode* tail = *pphead;while (tail->next->next != NULL){tail = tail->next;}free(tail->next);tail->next = NULL;}
}void SListPopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
{assert(pphead);assert(*pphead != NULL);//if (*pphead == NULL)// return;SLTNode* next = (*pphead)->next;free(*pphead);*pphead = next;
}SLTNode* SListFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x)
{SLTNode* cur = phead;while (cur){if (cur->data == x)return cur;cur = cur->next;}return NULL;
}void SListInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
{assert(pos);assert(pphead);// 头插if (pos == *pphead){SListPushFront(pphead, x);}else{SLTNode* prev = *pphead;while (prev->next != pos){prev = prev->next;}SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);prev->next = newnode;newnode->next = pos;}
}// 删除pos位置的值
void SListErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos)
{assert(pphead);assert(pos);if (*pphead == pos){SListPopFront(pphead);}else{SLTNode* prev = *pphead;while (prev->next != pos){prev = prev->next;}prev->next = pos->next;free(pos);pos = NULL;}
}// 单链表在pos位置之后插入x
void SListInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
{assert(pos);/*SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);newnode->next = pos->next;pos->next = newnode;*/// 不在乎链接顺序SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);SLTNode* next = pos->next;// pos newnode nextpos->next = newnode;newnode->next = next;
}// 分析思考为什么不删除pos位置?
void SListEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos)
{assert(pos);if (pos->next == NULL)return;SLTNode* del = pos->next;//pos->next = pos->next->next;pos->next = del->next;free(del);del = NULL;
}
